DOMAIN_TABLE
Description
The DOMAIN_TABLE function can be used to create a temporary table from various column(s), which can be used as a target table inside all PU-functions.
It is not possible to use the same table as the source and the target table in a PU-function. However, the DOMAIN_TABLE function can be used to create a temporary table from various column(s). These column(s) must have a common table to which the columns are joined to. The source column for the PU-function has to be from a common table of the specified column(s) for the temporary table. Further documentation about join relationships can be found in Join functionality.
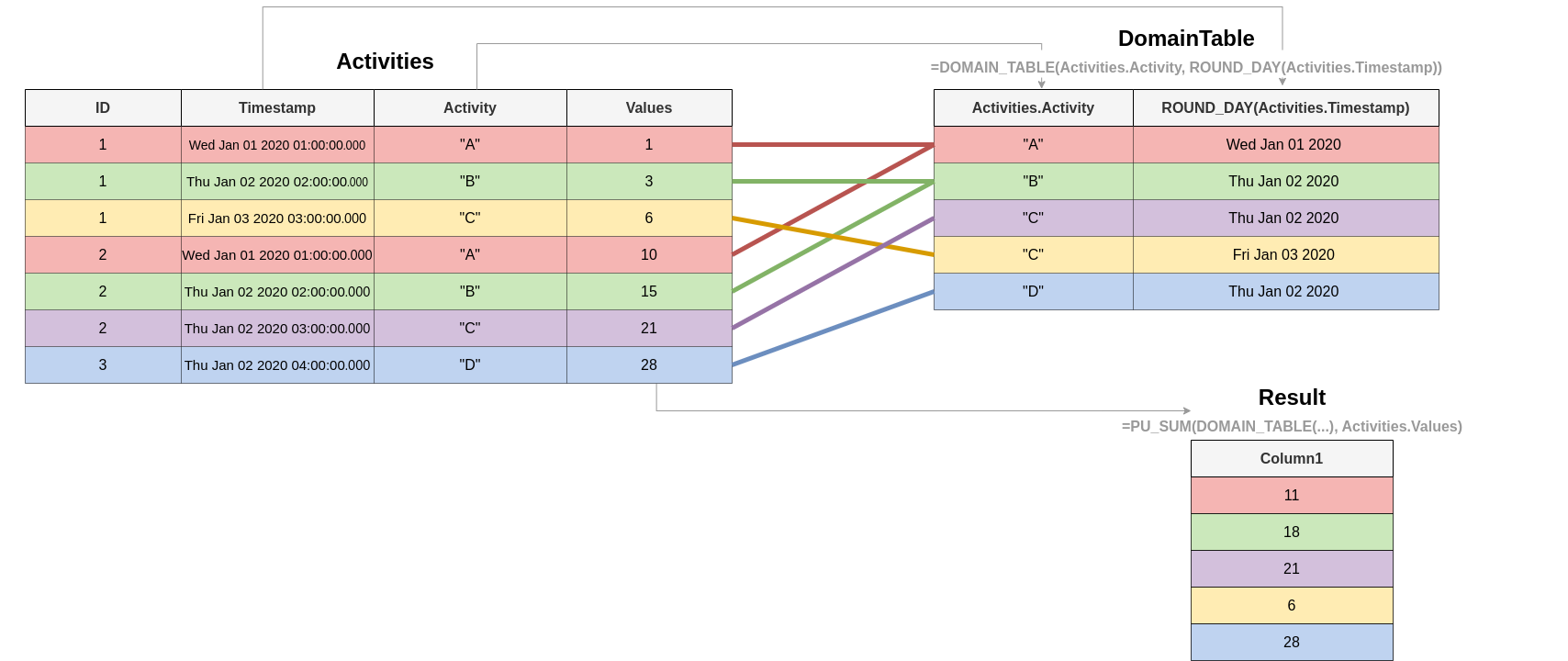
The temporary table created by DOMAIN_TABLE contains all unique combinations of values from the specified column(s) existing in the result of joining these column(s) to their closest common table. The resulting temporary table always has a 1:N relationship with that closest common table of the specified column(s).
In the following figure this concept is being visualized using the query:
PU_SUM(DOMAIN_TABLE("Activities"."activity",ROUND_DAY("Activities"."timestamp")), "Activities"."values"))For this, the DOMAIN_TABLE of all days and activities in the input table is created, and a grouping of equal activities on the same day for each distinct day and activity is made. The sum of the corresponding values is calculated with PU_SUM.
Syntax
DOMAIN_TABLE ( table.column, ... )
Use Cases
DOMAIN_TABLEcan be used for Fallback Status.DOMAIN_TABLEcan be used for Multiple Invoices per Case.
Examples
[1] For each case ID, calculate the number of times the associated company code is contained in the table using | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
[2] Filter on all cases where the associated company code occurs less than three times in the table: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
[3] In this example, the activity table is filtered on all entries that happened on a day with more than three actvities. For this, the | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
[4] This example is related to the figure in the overview. For this, the | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|