Types of insights
Association insights
Association insights tell you what subgroups of the data are underperforming in your metrics relative to the rest of the population. They also tell you how much the metrics could hypothetically improve by addressing the inefficiency.
 |
In the example insight above, a low Order Cancellation Rate is desirable. The Order Cancellation Rate considering all 242K orders in the data set is 16.2%. However, there are 5.54K orders for a particular customer GlobalHorizon Enterprises where there has been a Sales Order Regulatory Hold. The Order Cancellation Rate of this subgroup is 90.0%. This is much higher than the global average, suggesting there is room to improve. The improvement in the Order Cancellation Rate is estimated to be from 16.2% to 14.2%.
Cohort trend insights
Cohort trend insights reveal how your metrics change over time, as well as which cohorts drive (change in the same direction) or detract from (change in the opposite direction) those trends.
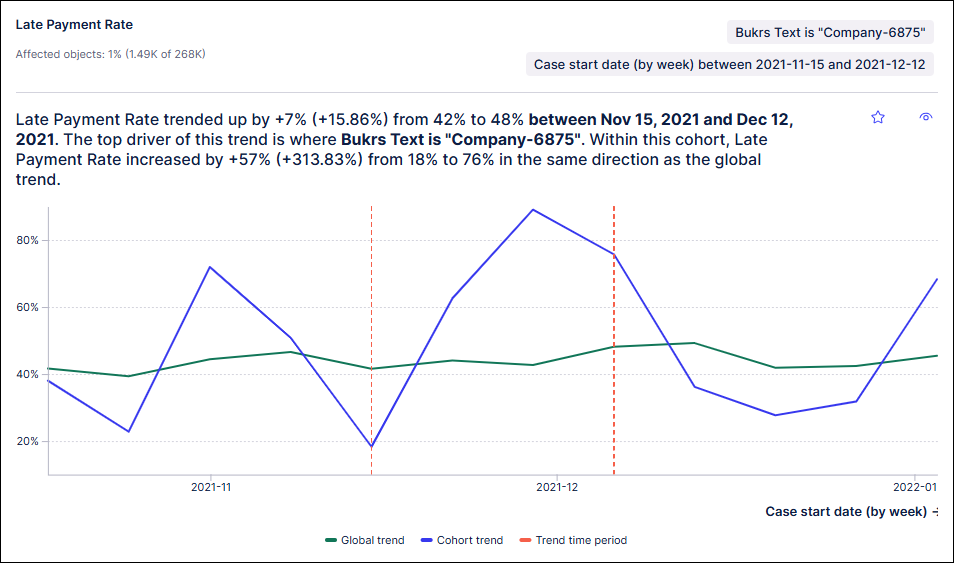 |
There are several important considerations for the using cohort trend analysis:
Only metrics utilizing an
AVGaggregation type are supported.An event log is required to construct the time series being analyzed.
This time series is constructed based on the timestamp of the first event per case.
Metrics using
FILTER_TO_NULLwill have limited support which can lead to issues resulting from the inconsistent propagation of filters.