Celonis Process Management BPMN reference
Note
This is a reference guide to BPMN icons used in Celonis Process Management.
BPMN overview
Type | Description |
|---|---|
Swimlane | Demonstrate organizational and technical responsibilities. |
Task | An atomic activity that defines a unit of work within a process. It has exactly one incoming and one outgoing sequence flow. |
Connection | Define the order in which tasks are performed. |
Gateway | Split or join the control flow. Best practice is to keep this differentiation hard so that a gateway either has exactly one incoming and several outgoing sequence flows or vice versa. |
Task types
Icon | Name | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
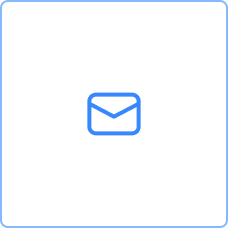
| Message task | Send or receive a message to or from a participant (eventually another BPMN pool). | |
| User task | Executed by a person with the assistance of a process-aware application. Typically performed via an application user interface. | |
| Manual task | Executed by a person without the aid of a process-aware application, often without user interface. Example: telephone call. | |
| Business rule task | Used to determine or calculate an output based on some input data. Examples: setting a priority, calculating cost. Often used before a gateway to decide on the right path. | |
| Service Task | No human interaction. Automatically executed by some sort of an external service such as a web service. | |
| Script Task | No human interaction. Executed by a process execution engine. Example: assigning a new helpdesk ticket to an operator. |
Task Marker
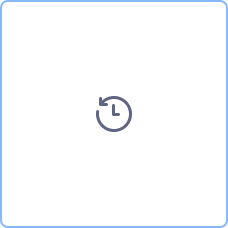
| Loop | Repeats a task until condition is true (like “WHILE). | |
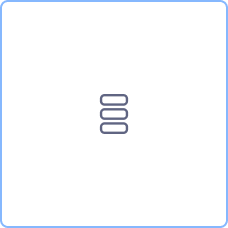
| Sequential multi instance | Sequentially executes a task for all items (like “FOR EACH”). | |
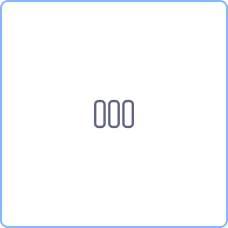
| Parallel multi instance | Instances are executed in parallel (like “FOR EACH”). |
Connections
 | Sequence flow | Defines the order in which tasks are performed |
 | Message flow | Indicates the flow of messages between pools |
 | Association | Links information (carriers) with other elements |
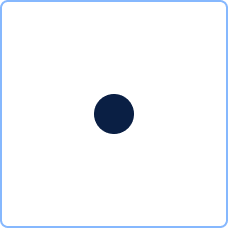
Events
 | Start event | Initiates the process. A process can have multiple start events. A start event has no incoming and exactly one outgoing sequence flow. |
 | Intermediate event | Indicates an event (that eventually needs to be waited for) within a process. It has exactly one incoming and one outgoing sequence flow. |
 | End event | Regularly ends or terminates the process. It has exactly one incoming and no outgoing sequence flow. A process can have multiple end events. |
Gateway types
Icon | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Exclusive | Alternative paths. Exactly one path is activated / consumed. | |
| Parallel | Combines or activates all incoming / outgoing paths. | |
| Inclusive | Indicates alternative but also parallel paths. One or several paths can be activated or consumed. |
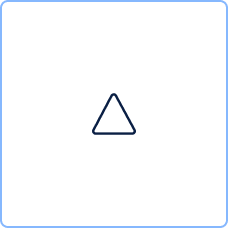
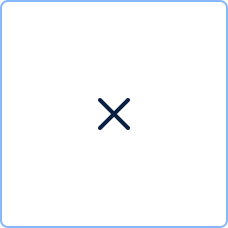
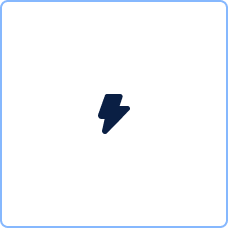
Event types
| Message | Receiving (catch) or sending (throwing) messages. | |
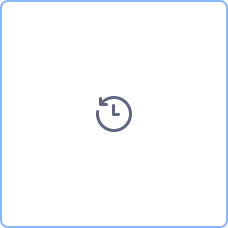
| Timer | Cyclic events, point in time, time spans or timeouts. | |
| Escalation | Escalation to a higher level process or responsibility. | |
| Conditional | Reaction on changed circumstance. | |
| Link | Connector between different points in a sequence flow (throw vs. catch). | |
| Compensation | Handling a compensation | |
| Signal | Receiving (catch) and sending (throw) signals across different processes. | |
| Cancel | Triggering cancellation or reacting to cancellation. | |
| Error | Catching or throwing errors. | |
| Terminate | Immediately terminates |
Tasks
| Task | As an atomic activity, the task defines a unit of work within a process. It has exactly one incoming and one outgoing sequence flow | |
| Call activity | Triggers a global process (refers to another BPMN model) | |
| Sub-process | Describes a task in a more detailed way (one level below). Sub-processes can be collapsed or expanded. |
Task markers
| Loop | Repeats a task until condition is true (like “WHILE) | |
| Sequential multi instance | Sequentially executes a task for all items (like “FOR EACH”) | |
| Parallel multi instance | Instances are executed in parallel (like “FOR EACH”) |