Set up SAP real-time extension
Real-time connection to SAP can be implemented for Full Cloud and Hybrid (LYDIP) scenarios.
Supported Databases
The following database are currently supported:
Oracle
DB2
MS SQL (2012 and higher)
SAP HANA
Sybase
The real time extension requires you to install Celonis RFC Module and Extractor.
For clean installation of the RFC Module and Extractor Service follow the steps as described Installing the RFC module.
The Real-time extractor setup mainly includes the following two actions:
Create the Log tables to store the changes in SAP
Install triggers to monitor the changes in SAP
This step has been simplified by including the Change Logs of the standard templates (O2C, P2P, AR, AP) in the transports of the Celonis RFC Module. This means that the customer who are installing the RFC Extractor the first time, can easily activate the Change Log tables for the respective process with a minimal effort, as described below.
Note
If you're migrating from SAP ECC to S/4HANA, before setting up your log tables, be aware that many traditional ECC tables have been replaced by simplified tables in the S/4HANA data model.
For example:
MATDOCreplacesMSEG,MKPF, and other related inventory tables.ACDOCAreplacesBSEG,COEP, and other financial/controlling line item tables.
Before configuring log tables for replication, we recommend checking if you are targeting outdated ECC tables, and switching to the S/4HANA-native replacement. For more information, see the following SAP documentation:
a) Creating Log Tables
The standard SAP landscape is comprised of 3 systems - DEV, QA and PROD. The Log tables can usually be created only in the DEV system, because the QA and PROD systems are locked for these kinds of changes.After the tables are added in DEV, they should be transported to QA and then to PRD via a transport. However, the triggers are not transportable, and should be installed in QA (for testing) and then subsequently in PRD (for productive use). The diagram below describes a typical setup process.
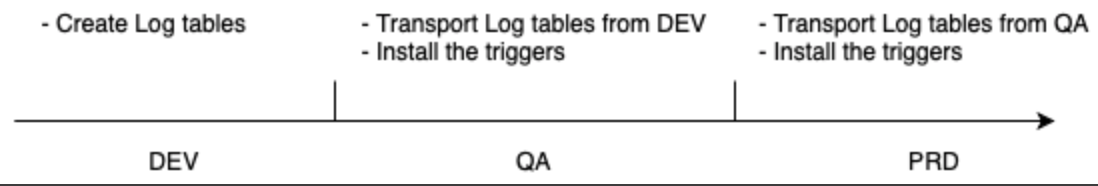 |
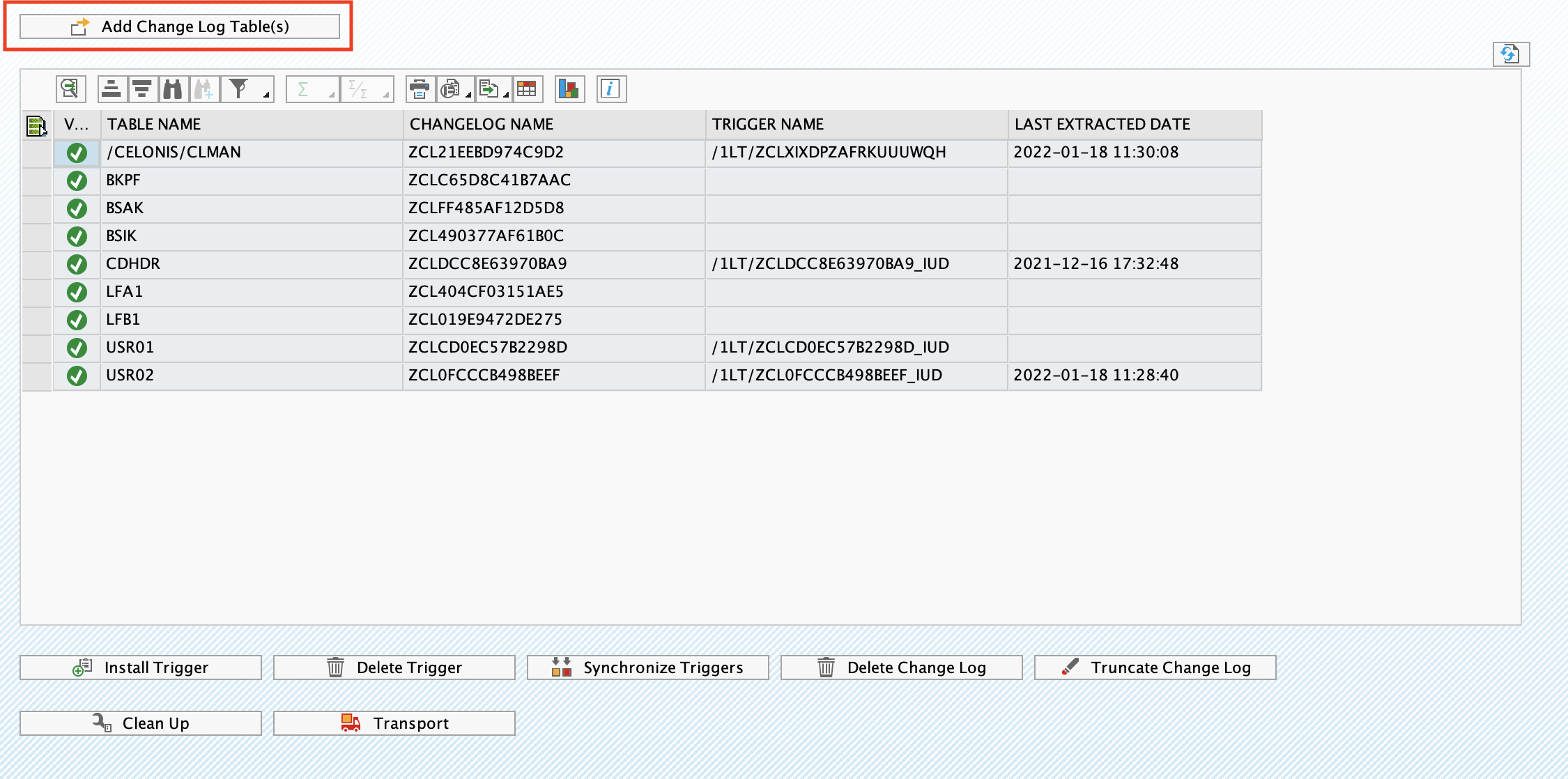
To add a Change Log table:
Log in into SAP and navigate to Transaction Code /CELONIS/CLMAN_UI.
Click the Add Change Log Tables button.
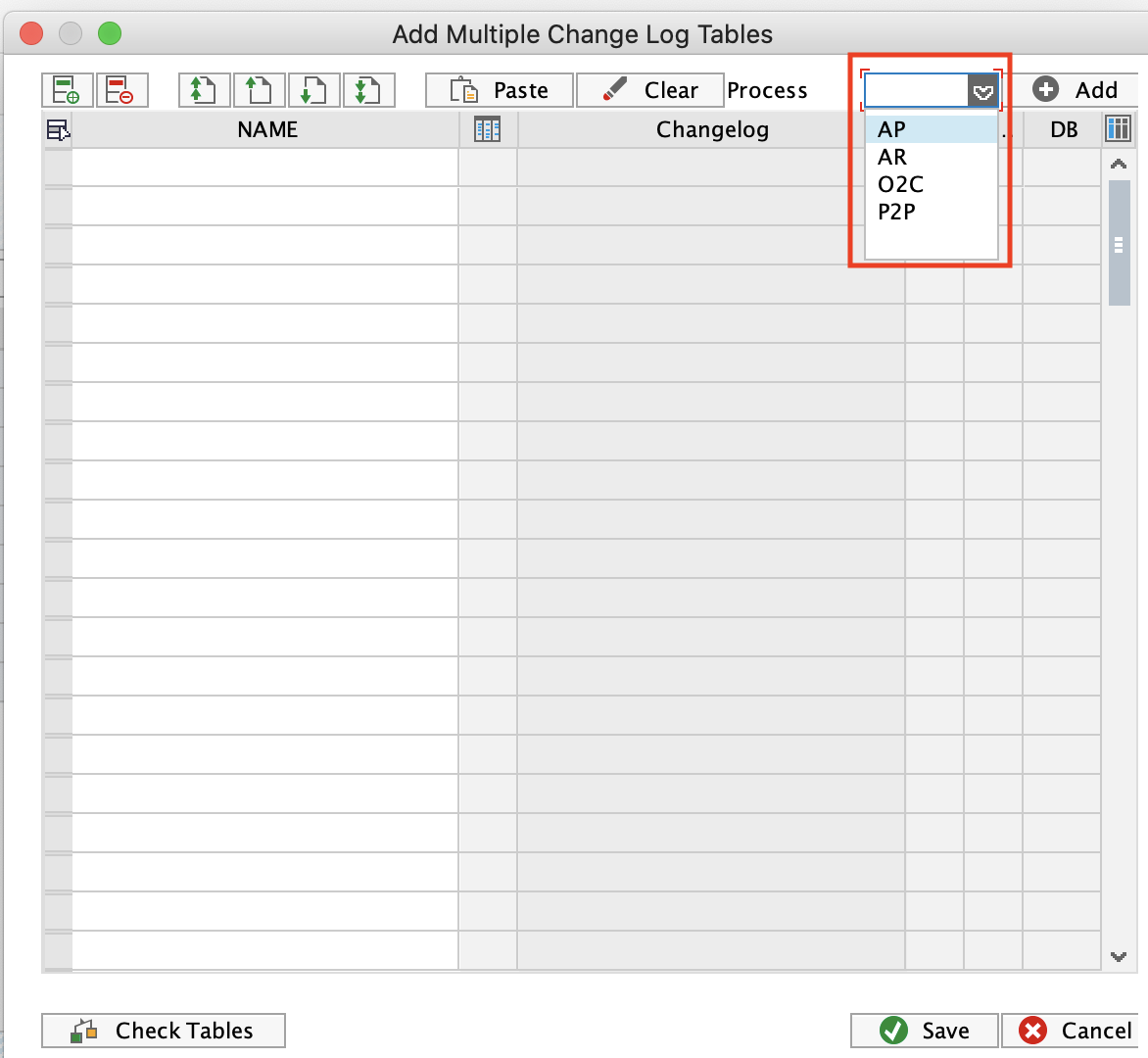
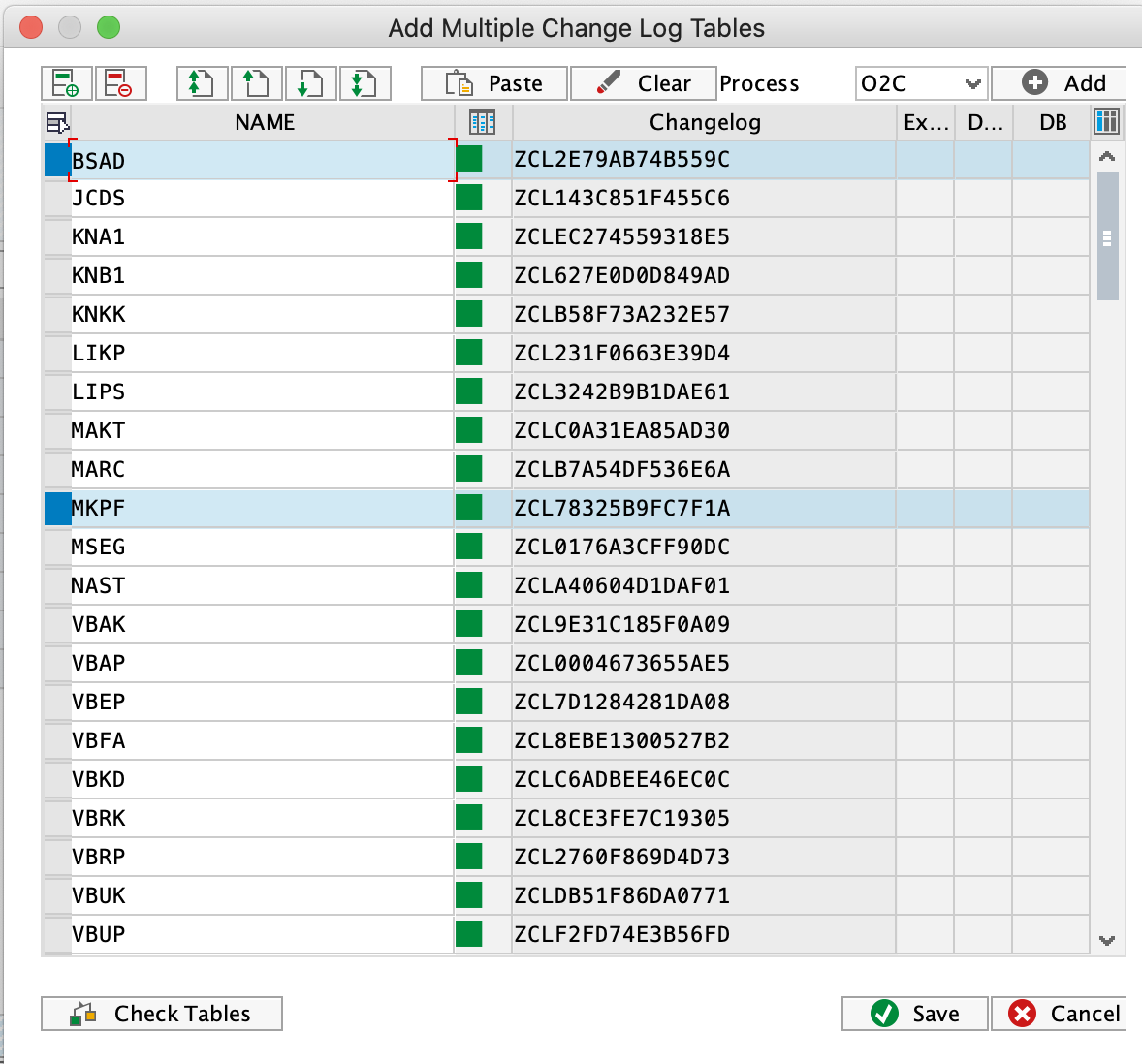
In the pop up select the process you want to activate. The respective tables will be populated in the screen.
Click Check Tables to dry run the creation process. If everything is green, click Save, and the Change Log tables will be added.
 |
 |
 |
After the tables are created, you will need to transport them to the next system as described inn the next section.
Required SAP rights to add log tables and triggers
The SAP User should have minimum the following rights to be able to create the tables and add triggers. However, usually this action is performed by SAP BASIS who has full admin rights.
To access /CELONIS/CLMAN_UI and install triggers
Object: S_TCODE
TCD: /CELONIS/CLMAN_UI
To create/delete Change Log tables
Object: S_DEVELOP
ACTVT: *
DEVCLASS: ZCELONISCL
OBJNAME: *
OBJTYPE: TABL
b) Transporting the Change Log Tables Forward
To streamline the transfer of CL tables from DEV to either of QAS or PRD, the T code /CELONIS/CLMAN_UI allows the user to generate a transport that carries forward the setup configurations to the next system in the landscape.
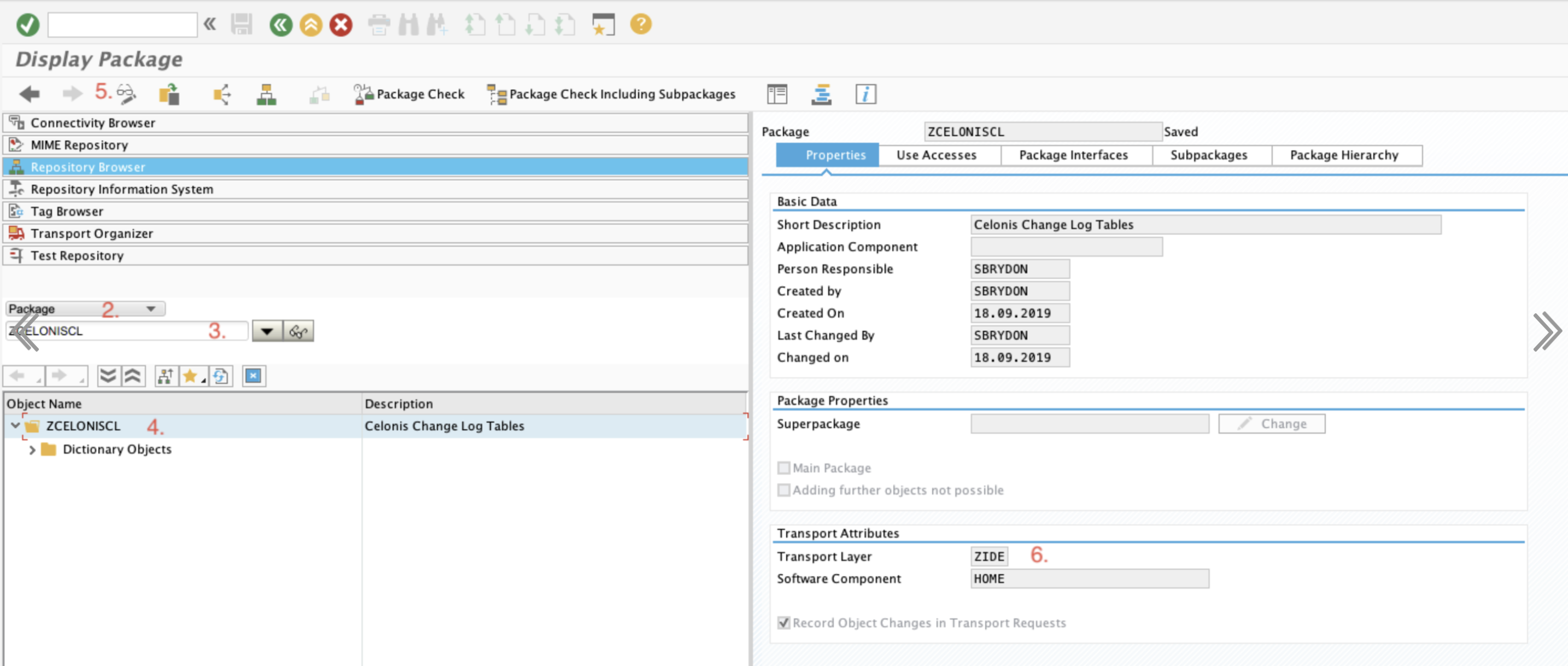
Before creating the transport in DEV, the SAP BASIS admin should change the Transport Layer of the package ZCELONISCL. Make sure to select a Layer that contains a Consolidation Route connecting DEV to QAS. This will ensure that the log tables can be assigned to a transportable request, and therefore, be pushed forward from DEV to QAS. To change the layer:
Call SE80 to open the Object Navigator.
In the object list selection, choose Package.
Enter ZCELONISCL and choose Display.
Double-click the name of the package.
Switch to edit mode.
Select a Transport Layer that contains a Consolidation Route connecting DEV to QAS.
 |
Tip
After saving the Transport Layer change, you may be prompted to transport that modification too. However, this change is not needed in QA/PRD so you don't need to transport it.
After performing the steps above, create a transport request for the Change Log tables:
Call the transaction code /CELONIS/CLMAN_UI
Select the Change Log tables that you want to transport forward and click Transport.
You will be prompted to select or create a transport.
The selected tables will be added to the transport request, which you can release to the next system.
c) Creating Triggers
A trigger should be installed to track the changes in the source tables, and capture them in the respective Change Logs. To do that:
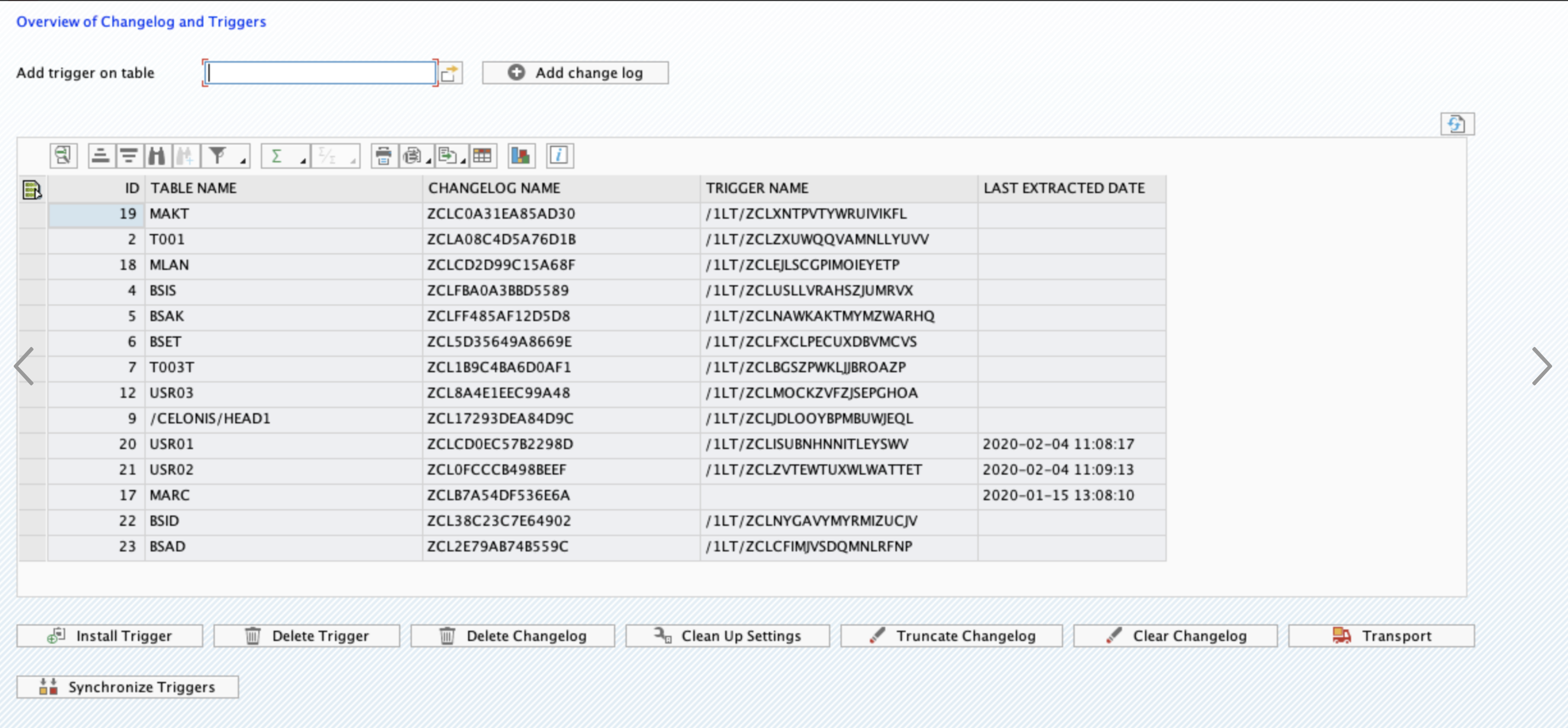
Log in into SAP and navigate to Transaction Code /CELONIS/CLMAN_UI.
Find the table(s) in the grid (check this section for the steps on how to add a table).
Click Install Trigger.
After the trigger is installed successfully, its name will be displayed in the “Trigger Name” column.
After these steps are completed successfully, the Delta Extractions for the specified tables will be executed in real time mode. The date and time of latest successful execution will be displayed in the column “Last Extracted Date”.
 |
Warning
Triggers cannot be transported. They should be installed in QA (for testing) and then subsequently in PRD (for productive use).
d) Activating the Clean Up Background Job
In the CL Management UI you can set up a recurring background job in SAP which will run on a daily basis and clean up the records from the Log tables.
To setup the job click the Clean Up Settings button.
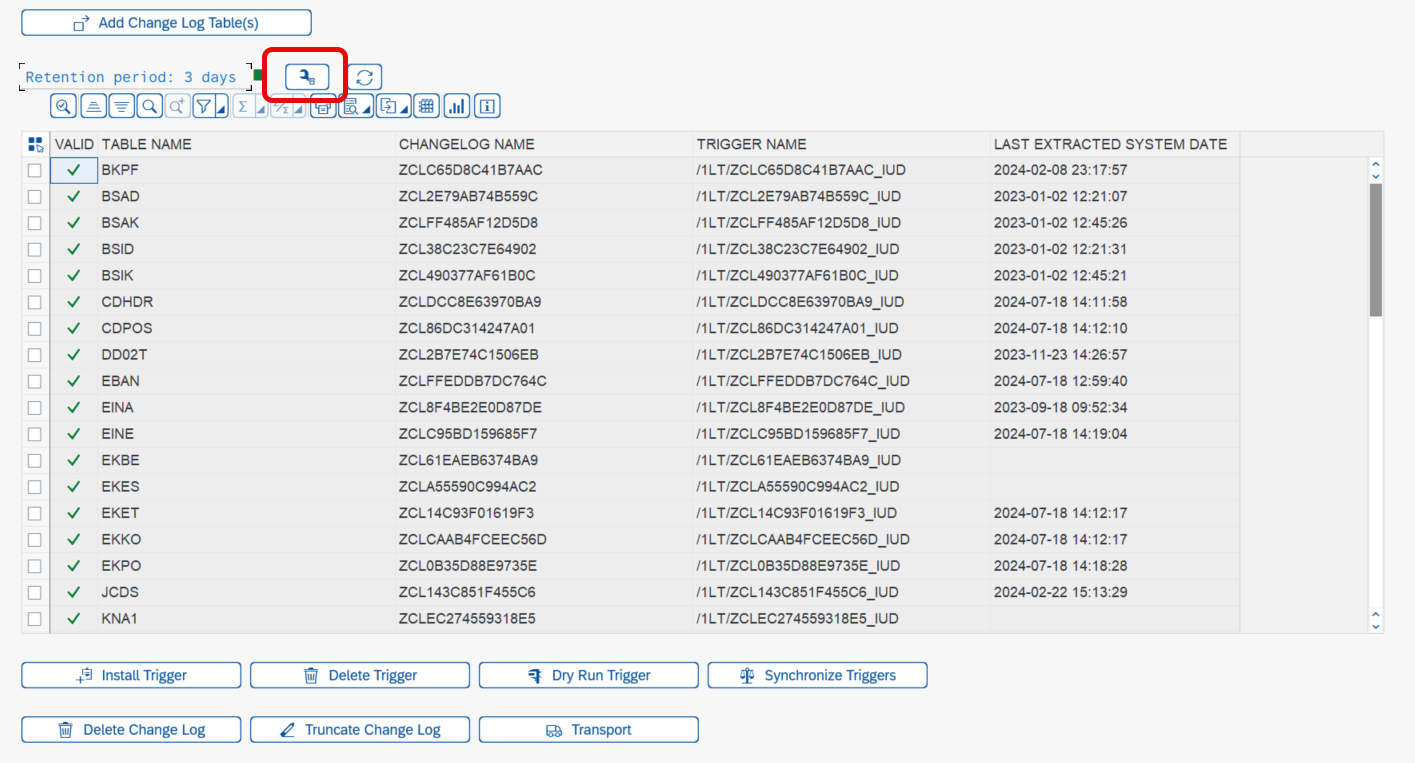
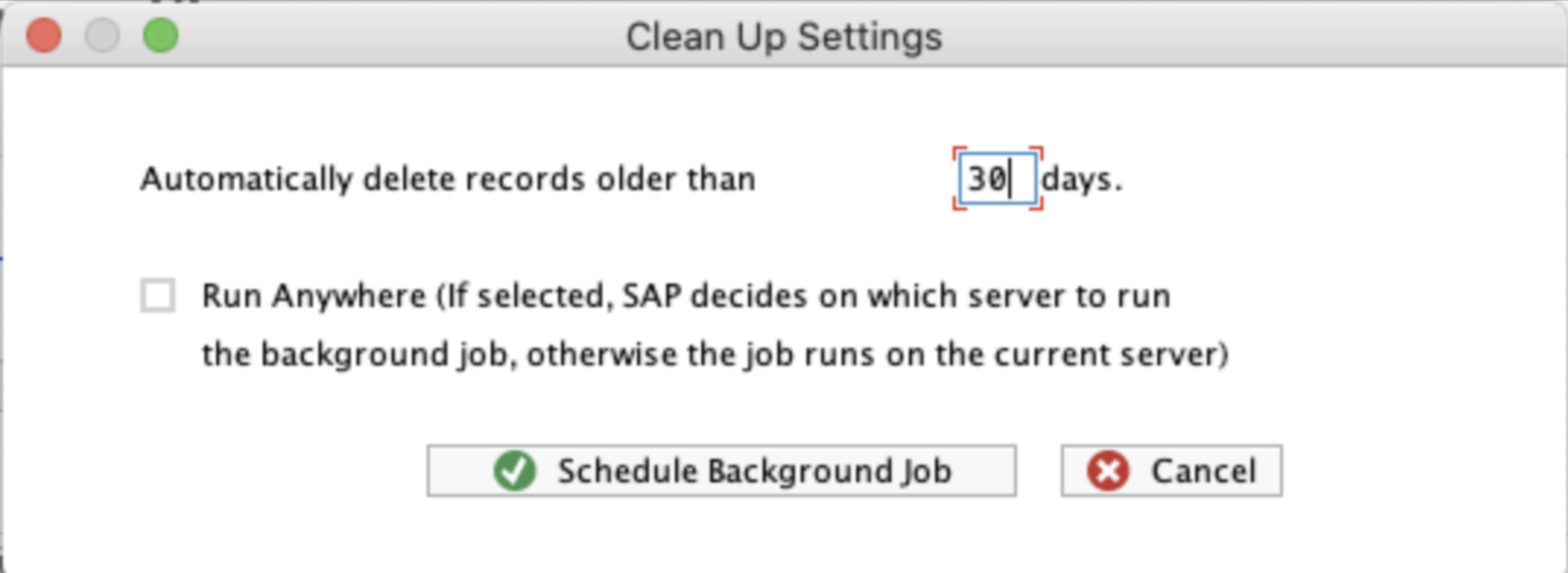
A dialogue will pop up where you should define:
Number of days to keep records also called the retention period. All records older than the specified date will be removed from the log tables. The retention period value is displayed above the change view. If the value is "N/D", it means that that there is no background job configured.
Where to run the background job. If the "Run Anywhere" option is selected, SAP system will decide on which server to execute the job. Otherwise, the job will be run on the same server where the settings have been defined.
 |
Warning
The clean up background job is an important element to control the size of the Log tables. It prevents the tables from growing in case they are not being extracted.
Adding and deleting change logs
In some scenarios you may need to add new tables to an existing setup or remove unnecessary ones.
Adding change log tables
Add the new change log tables in the QA system.
Assign the selected tables to a transport and move them forward to the next environment.
Deleting change logs
In this scenario the goal is to remove tables from the production environment. The process involves two steps: remove the triggers and delete the change log tables.
The triggers are not DDIC objects, so you won't need to open the client for these changes. They can be removed directly in the production system using the /CELONIS/CLMAN_UI transaction code.
Once the triggers have been removed, you will also need to remove the change log tables. This step should NEVER be done directly in the production system. The tables need to be manually deleted in your development server and assigned to a transport. This transport will then be moved on towards production to remove the tables from that server as well.
Warning
Make sure that the development system is an exact copy of the production system. If you want to remove the change log tables X, Y and Z from production, then you need to have the exact same tables in the development system so that you can delete them from the development sever first.
Note
You will need a developer key to perform the deletion. This is a standard SAP rule and cannot be skipped.
Name the transaction code
/CELONIS/CLMAN_UI.Select the change log tables that you want to delete and then click Delete Change Log.
You will be prompted to select or create a transport. The deleted tables will be added to the transport request, which you can release to the next system.
Once the transport is moved to production, the change logs will be removed from the production server. You can verify that they have been deleted by opening the
/CELONIS/CLMAN_UIscreen.
The trigger creation command is executed from a SAP GUI (transaction code /CELONIS/CLMAN_UI), however, the trigger is created only at the database level executing native SQL command. In other words, the trigger does not exist in the SAP Data Dictionary. Therefore it cannot be transported and should manually be created in each environment.
Triggers generate a logging entry for each transaction in SAP, so there is some impact. However, the impact is very small and does not slow down operations.
Triggers are a native database technology and therefore they are very effective. They are not a technology created by Celonis, and we just instruct the trigger when and how to react.
Before starting the data migration you can delete the triggers, and then re-install them once the migration is over.
Triggers operate at the database level, and whenever the database record is inserted/updated/deleted the trigger works. The trigger responds to all field updates, and it does not distinguish between the standard SAP and custom (Z) fields. For any update a log record will be generated.
When setting up the triggers you should also create the Clean Up job, which is basically an SAP Recurring Background Job that runs on a daily basis and removes the extracted records that are older than X days, where X is defined by you. This makes sure that the tables are regularly purged and consume minimal space.
The real time extractor uses its own triggers which will not interfere with those of SLT. Both can be run in parallel.