HTTP (On-Prem) (Action Flow)
The HTTP app provides various modules for communication based on Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web.
Getting Started with HTTP (On-Prem)
The right choice of the module depends on the authentication/authorization mechanism the resource you wish to access uses:
Make a HTTP request- universal module to make an HTTP request to an on-premise system and process the response.
Make a Basic Auth request - this module allows you to send an HTTP request with the basic authentication. The output bundle contains the HTTP response.
Make a HTTP request
A universal module to make an HTTP request to an on-premise system and process the response.
This module requires the Celonis on-prem client.
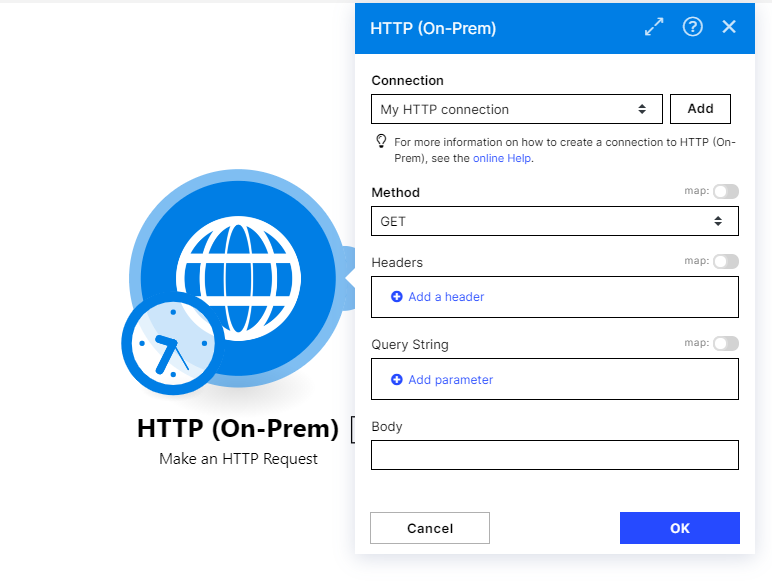
1. System connection
System Connection Name | Define a name for your new system connection e.g. HTTP POST ABC |
URL | Enter a URL you want to send a request to, e.g., API endpoint, website, etc. |
2. App configuration
Method | Select the HTTP method you want to use e.g.: GET to retrieve information for an entry. POST to create a new entry. PUT to update/replace an existing entry. PATCH to make a partial entry update. DELETE to delete an entry. |
Headers | Enter the desired request headers. For example, an authorization. By default, the request does not contain the |
Query String | Enter the desired query key-value pairs. |
Body | HTTP Body is the data bytes transmitted in an HTTP transaction message immediately following the headers if there are any to be used. Note
|
Tip
You can parse the respone by using e.g. JSON or XML Parser after the HTTP module.
Make a Basic Auth request
The Make a Basic Auth request module allows you to send an HTTP request with the basic authentication. The output bundle contains the HTTP response.
Credentials | Click Add to add your credentials (user name and password) for basic authentication. | ||||||
Evaluate all states as errors (except for 2xx and 3xx) | Use the response status to detect errors. Otherwise, the module reports only Make related errors (like mapping errors or missing required values). | ||||||
URL | Enter the request URL. | ||||||
Serialize URL | Encodes the API call URL with the URL encoding (encoding special characters for example). | ||||||
Method | Select the HTTP method you want to use:
| ||||||
Headers | Enter request headers. For example, the response content type. Caution The HTTP app requests do not have the Accept header. If the HTTP request returns an unexpected response, try adding the | ||||||
Query String | Enter the query key-value pairs. | ||||||
Body type | HTTP
| ||||||
Parse response | Enable to parse HTTP responses into bundles. With this option, you don't need to add the Parse JSON or Parse XML modules. Otherwise, the HTTP module returns the raw response data. Before you can use parsed JSON or XML content, run the module once manually so that the module can recognize the response content and allow you to map it in subsequent modules. | ||||||
Timeout | Specify the request timeout in seconds (1-300). Default: 40 seconds. | ||||||
Share cookies with other HTTP modules | Enable to share cookies from the server with all HTTP modules in your Action Flow. | ||||||
Self-signed certificate | Upload your certificate if you want to use TLS using your self-signed certificate. | ||||||
Reject connections that use unverified (self-signed) certificates | Enable to reject connections that use unverified TLS certificates. | ||||||
Follow redirect | Enable to follow URL redirects that return 3xx response statuses. | ||||||
Follow all redirect | Enable to follow URL redirects regardless of response statuses. | ||||||
Disable serialization of multiple same query string keys as arrays | Celonis platform handles multiple values for the same URL query string parameter key as arrays (e.g., | ||||||
Request compressed content | Enable to request compression of the response data. Adds the | ||||||
Use Mutual TLS | Select if you want to use mutual TLS (mTLS) for the HTTP request to ensure both the client and server authenticate each other using certificates. |