Labels in Task Mining
Task Mining labels overview
In Task Mining, labels are attributes that are assigned to events to add context. You use labels to help organize and contextualize events and simplify analysis. For example, you could a label for an application, screen, or document name to an event, such as Login.
You use different label types depending on the data you want to enrich. You can assign default, predefined labels to commonly-used applications, screens, or documents. These labels help you organize and contexualize how data from those applications, screens, or documents are displayed in your project data. Default labels are generally assigned to standard applications like Microsoft Excel or Microsoft Word, but you can also can override default labels with custom labels.
For example, you could override the default, predefined label Microsoft Excel with a custom label of Excel. Custom labels use rules to determine where they should be applied, such as 'application equals winword' or 'URL contains salesforce'.
If a screen or application does not have a default label assigned, it will display in your data without a name until a custom label is created for it.
Naming conventions
Label - A Label is a user-defined identifier applied to Task Mining data elements for understandable naming. Labels create richer semantic abstractions and facilitate data interpretation. For further information, see Label naming guidelines.
Label Rule - Specific conditions to determine how and when a label should be applied to Task Mining data during processing.
Default Label - Default labels are predefined labels provided out-of-the box. They provide a standard naming convention for common applications and screens and can be replaced by Custom Labels.
Custom Label - User-defined identifiers assigned to Task Mining data for clarity and to reflect naming conventions, replacing default labels, and configured via the Label Editor.
Label Editor - A user-friendly interface within the Task Mining tool that allows users to create, manage, and apply custom labels to their data without the need for programming skills.
Data Configuration - A section within the Task Mining tool where users can set up and modify how their data is processed, structured and labeled to simplify the analysis process later.
Default labels
Celonis provides a default set of matching rules for popular apps (detailed list of supported apps below). They include the most common Google apps, Microsoft Office apps and SAP Logon.
They are aimed at setting easy to understand values for Application, Screen and Document (where applicable) in the captured data.
These rules are applied before custom rules so it’s always possible to overwrite the default rules behavior if so desired.
To override your default labels, refer to Working with custom labels for more information.
Label sources
Source | Description | Customizable by user? |
|---|---|---|
Label | Generated 'out of the box'. | Yes. For more information, see Label naming guidelines. |
Raw | Attribute is captured in Task Mining client and copied over from the raw event. | No. Attributes captured are defined in client settings. |
Computed | Automatically created during processing. | No. |
Label types
Note
This table shows example information only. The availability of attribute values will depend on the client settings defined, technical availability and whether default or user-defined labels cover the event.
Label type | Source | Description | Further information |
|---|---|---|---|
Application | Label | User-friendly name of the software application or website where the event occurred provides context for the event and helps analyze user behavior across different tools and platforms. By default:
Note We also provide ‘out-of-the-box’ coverage for common, standard applications such as Microsoft Office or SAP. | You can add custom labels to define easy to understand and readable names. For example, Adobe Acrobat PDF Reader instead of Acrord32. For information on naming, see Label naming guidelines. |
Document | Label | Document name in applications like Word, Excel, PowerPoint and predefined for standard applications. Using a simple pattern syntax, users can define specific document names | Users can group similar document names together using the Screen label. This helps clarify the total time spent creating documents with a specific name. For example, you could create a Screen label called Order Report Documents and use this for all Excel documents named Order_Report_{date}. |
Screen | Label | Screen name within an application. This is most useful for applications with many screens, with screen names predefined for common, standard applications like SAP. Typically only used for important applications.NOTE: If the application is focused on documents, for example, Excel, Screen names are not defined as most time is spent on the main view which is the document.Grouping events by Screen simplifies analysis by clarifying which screens most time is spent on and what is happening in those screens. | If Document is defined but Screen is not, Screen can be set in the application to the document value which is helpful for Excel, Word etc. Using a simple pattern syntax, users can control how specific screen groupings are and provide them with names that are easy to understand and read for anyone using Celonis analysis in their organization. For example, the the Workday screen is defined by URLs like: *.workday.com/create-invoice/*”. Example: Create Sales Order in SAP or Create Invoice in Workday. |
ActiveWindow | Raw | Window name displayed at the top of every window and is generally the name of the application or website or further details. Taken from the window related to the user interaction event. | Configured in client settings and set by default to pseudonymize Windows username. |
Caseid | Computed | Concatenation of TimestampLocal and SessionId. Used in the PDD export and to show hops between applications in Studio | Deprecation and replacement with SessionID planned in Oct 2024. |
ClipboardContent | Raw | Textual content stored in the Windows clipboard. | |
ClipboardContentId | Raw | Unique identifier assigned each time the clipboard content changes (EventType = 'Clipboard changed'). Used to count clipboard copy operations and to create a PQL domain table for tracking clipboard copy and paste actions in Studio. | Set to the event ID at the time of the change. All subsequent events within the same recording session share the same ClipboardContentId until the clipboard content changes again and a new ClipboardContentId is assigned. |
CustomX | Raw | Optional custom user attribute that can be defined in the configurations to be entered by users, for example, the team name. | For more information, see Task Mining team insights. |
DomainName | Computed | Domain part of a URL where the raw event has a URL attribute. If the raw event has a URL attribute, the DomainName is the domain part of the URL. | For example, for URL https://www.google.com/search?q=test, the DomainName is www.google.com. |
EventDescription | Computed | Human-readable event description created byconcatenating a number of attributes. | For example, In Gmail, left click on Send button. |
EventType | Raw | Event type:
| For more information, see details of available event types. |
KeyboardCommand | Raw | Command key or key combination. | |
MousePositionX | Raw | Visualizes the X-coordinate of the mouse pointer’s position in a screenshot. | A negative value indicates that the mouse pointer is outside of the screenshot. |
MousePositionY | Raw | Visualizes the Y-coordinate of the mouse pointer’s position in a screenshot. | A negative value indicates that the mouse pointer is outside of the screenshot. |
ProcessName | Raw | Name of the application’s Windows OS process that was active when the user interacted with the computer. | Typically this is the ‘technical application name’, such as ‘saplogon’. See how to discover a process name for a specific application. |
ScreenshotId | Raw | File name of the screenshot related to the event, if screenshots have been optionally captured. | |
SessionId | Raw | Unique ID of the Task Mining session where a session is the period of time from starting to stopping Task Mining. | Starting and pausing can be done by the user via the start/stop buttons or automatically depending on settings. |
SystemUser | Raw | Windows user name of the active user who interacted with the computer. | Pseudonymized by default. Can be configured in client settings. |
TimeDelta | Computed | Amount of time the user ‘spent’ on an event, calculated in seconds based on the timestamp of the next event minus the timestamp of the current event. | |
TimestampLocal | Raw | When the event was detected in local time. | |
TimestampUTC | Raw | When the event was detected in UTC. | |
Url | Raw | URL of the website that is currently opened in the tab that triggered the event. | Availability depends on the application used, see data collection capabilities. |
UserId | Raw | Hashed Windows user name of the active user. | The value is hashed using SHA256. |
Label naming guidelines in Task Mining
Label names should:
Be coherent.
Reflect the official vendor application name.
Use full names rather than short names, so Microsoft Word, for example, and not Word.
Important
Where apps have both standalone and browser versions, both versions should have the same label name.
Required client settings in Task Mining
For the default rules to work, the Task Mining clients need to capture the relevant fields. If these settings are not applied, your Task Mining project will not be able to apply the default labels to the data collected or utilize custom labels.
Basic settings
Note
Currently you cannot capture SAP details using the Basic settings. If you need to capture information in SAP, use the Advanced settings configuration below.
If you use basic settings, please ensure the following:
Go to Client Settings and select "Use basic settings".
Scroll down to the Captured Details section and use the toggle to enable the “Name of active window or web tab” option.
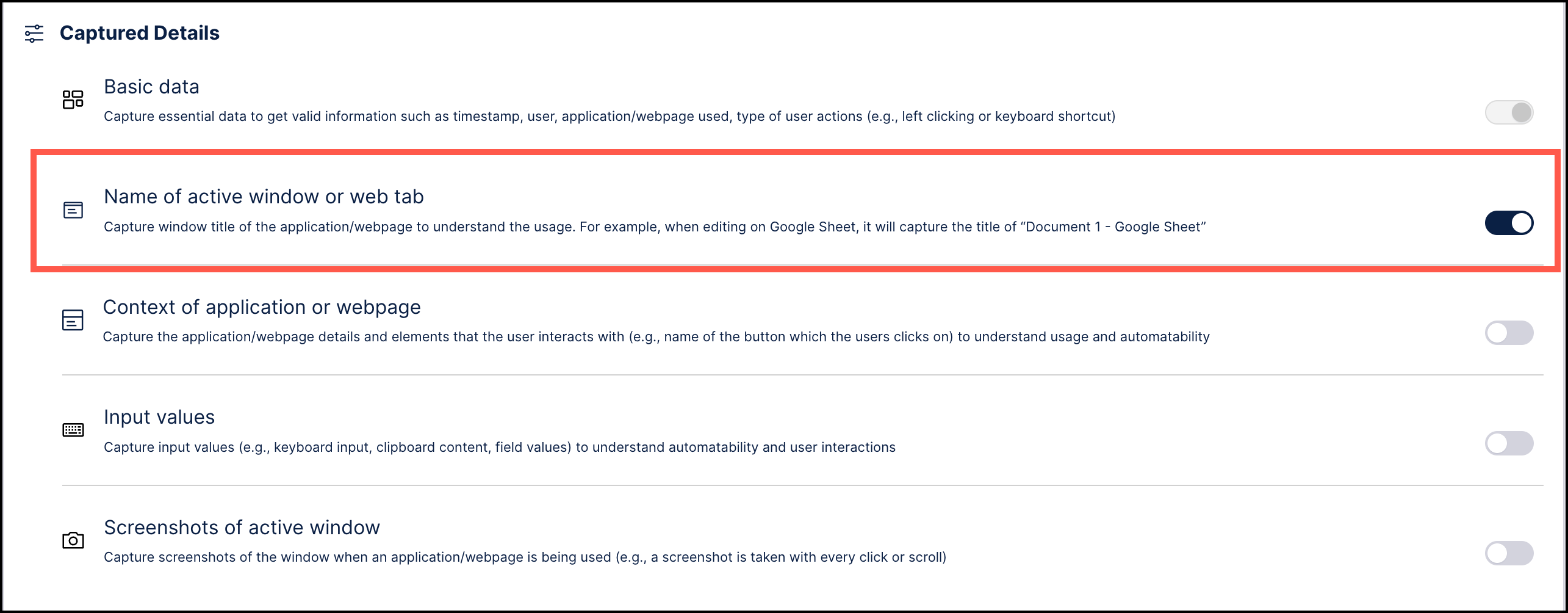
Click the Save Client Settings button in the upper right to apply the change.
The default labels will now be applied to the Supported applications in your project data. You can also create custom labels to override those default names or to apply to screens and applications without a default label.
Advanced settings
If you prefer to use advanced settings, please ensure the following:
Go to Client Settings and select "Use advanced settings".
Click the Configure settings button. and follow the setup wizard.
In Event Processing Rules, select the default rule “Log Events” and then click edit.
On the Event tab, select “All” from the dropdown.
On the Logging tab, select “All” or make sure that the following are captured:
For most labels:
ActiveWindow
URL
ProcessName
To also cover SAP Logon:
Make sure to allow TransactionSAP
Ensure SAP is set up correctly.
Enable the “Use Native URL Retrieval” option.
Click the Save Client Settings button in the upper right to apply the change.
The default labels will now be applied to the Supported applications in your project data. You can also create custom labels to override those default names or to apply to screens and applications without a default label.
Supported applications
The applications, screens and documents in the tables below have a default label assigned that is used when referring to any activity captured by the Task Mining client in those applications/screens/documents. This label indicates how applications/screens/documents will display within your data. If a default label has not been assigned, the applications/screens/documents will display without a name until a custom label is assigned.
Legend
N/A: Field extraction does not make sense, such as SCREEN for document based apps.
Unavailable: Field extraction would make sense but cannot (easily) be extracted from the current captured data.
Google Apps
Name | URL | Application | Screen | Document |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Gmail | mail.google.com | Supported | Supported | Supported |
Google Calendar | calendar.google.com | Supported | Unavailable | N/A |
Google Slides | slides.google.com/presentation | Supported | N/A | Supported |
Google Meet | meet.google.com | Supported | Supported | Supported2 |
Google Drive | drive.google.com | Supported | Supported | N/A |
Google Sheets | docs.google.com/spreadsheets | Supported | N/A | Supported |
Google Keep | keep.google.com | Supported | N/A | Unavailable |
Google Search1 | google.com/search | Supported | Unavailable | N/A |
Google Maps | maps.google.com | Supported | Unavailable | Unavailable |
1 - Google Search rules support arbitrary top-level domains.
2 - Google Meet: Document is set to the meeting key.
All languages are supported unless otherwise specified. Internal test data uses English and German.
Google Drive Screen value examples: My Drive, Search results, Create new folder, Shared with me, etc.
Gmail Screen value examples: Inbox, Write Message, Settings, Search results, etc.
Microsoft Office Apps
Name | Application | Screen | Document |
|---|---|---|---|
Microsoft Teams | Supported | Supported | N/A |
Microsoft Word | Supported | N/A | Supported1 |
Microsoft Excel | Supported | N/A | Supported1 |
Microsoft PowerPoint | Supported | N/A | Supported1 |
Microsoft Outlook | Supported | Supported | Supported1 |
Microsoft OneNote | Supported | Unavailable | Unavailable |
1 - Due to technical limitations, the document name may sometimes also contain non-document items, such as “Open” when the file open document is active.
OneDrive is not included because it has no UI.
For Microsoft Outlook, the document is populated with the subject when writing a message.
SAP Logon
Name | Application | Screen | Document |
|---|---|---|---|
SAP Logon | Supported | Supported | Unavailable |
SAP Logon refers to the SAP GUI for Windows.
Screen is mapped to the transaction code and requires that the TransactionSAP and WindowNameSAP attributes are captured in your data. See the Advanced settings section above for instructions on how to enable these attributes.