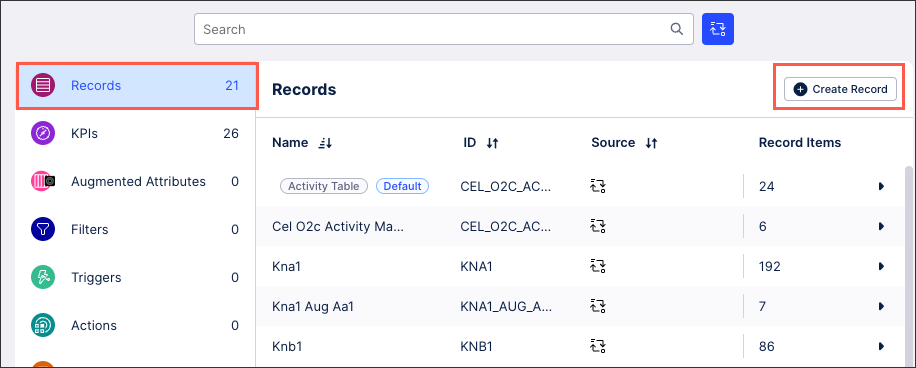
Knowledge Model - Records
Records contain all the domain and use-case-specific data for a Knowledge Model.
For instance, an Execution App in the domain of Accounting will typically have a Record for invoices. An Execution App in Customer Support typically has a Record for support tickets. Records are derived from tables in a Data Model, but have an additional layer of abstraction. In comparison, a Data Model table contains the actual data instances in a certain schema (Data Model Layer), whereas a Record features more powerful modeling capabilities such as human-readable annotations (e.g. Display Name and Description) as well as Augmented Attributes.
Records and attributes are frequently used in tables, action flows, skills, and in many other components.
Creating records in the Knowledge Model
Within the Knowledge Model, the records assets include a human-readable name, an ID, its PQL formula, and a description.
To create a record:
Click Studio and then open the package containing the Knowledge Model you want to create the record in.
Open the KM you want to create the record for.
Select Records and then click Create Record.
Configure your record using the following settings:
Display Name: A human-readable label used in the user interface.
Short Display Name: Shorter human readable label for the object shown automatically on the Views whenever the Display Name is truncated. Can contain max 20 characters.
ID: A unique technical identifier used to reference this record. Must be unique within all Records in the KM.
Description: A human-readable description for the record.
Internal Note: A field only visible within the KM.
PQL Formula: Contains the reference to the table in the data model that will be represented in the record.
Click Save.
The record is added to your KM and available to use in your related content.
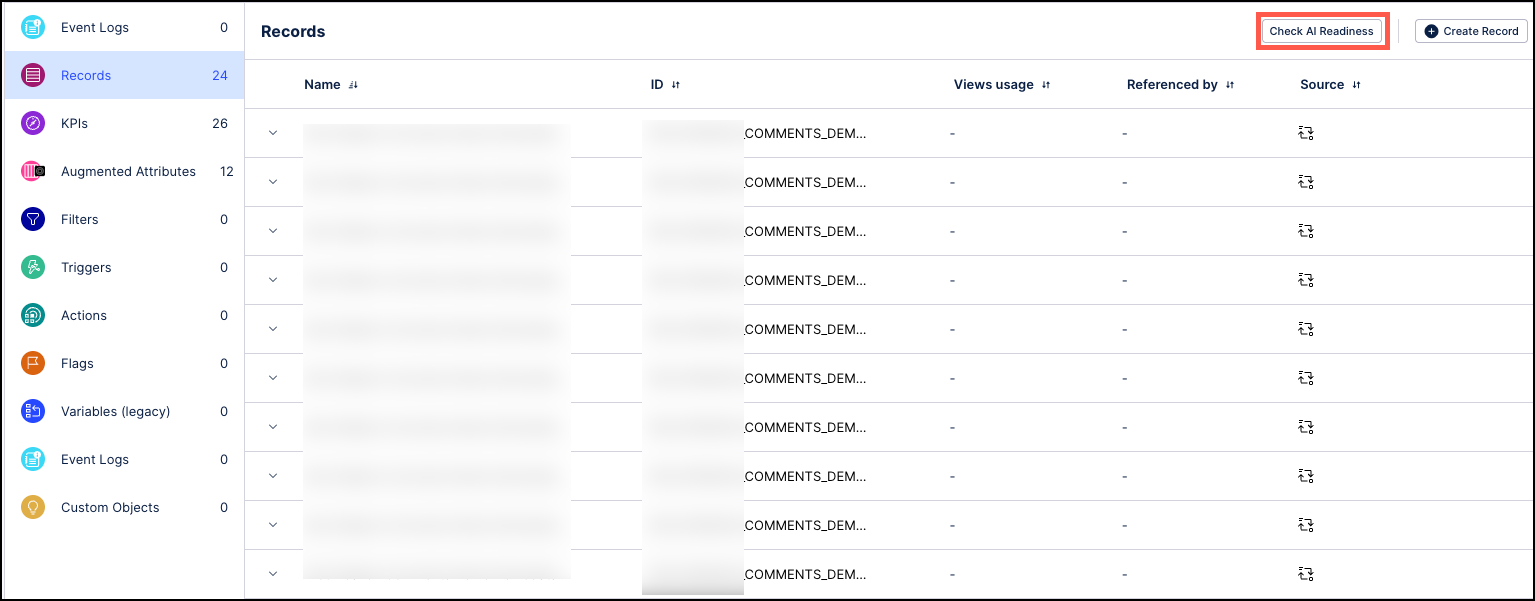
Check the AI readiness of Knowledge Model attributes
The Check AI Readiness button is used to scan your Knowledge Models and check if they ready to be used with AI tools such as Process Copilot or Insight Explorer. These scans check the record attributes in your Knowledge Models for issues such as missing descriptions, duplicate entries, outdated attributes, and other problems. These issues could potentially cause issues with your AI tools if they are analyzing inconsistent or incomplete data which can impact the quality of your outputs.
 |
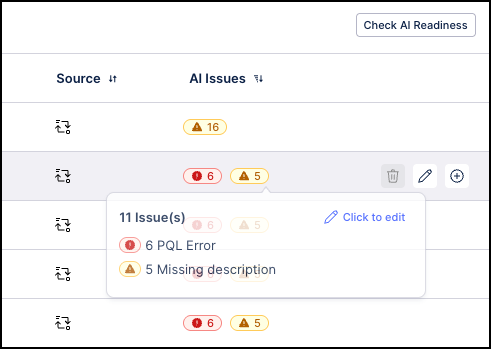
If any errors or warnings are detected by the scan, the AI Issues column displays icons indicating the total number of errors (red icon) and warnings (yellow icon) for each record. You can hover over any warning or error icon to see a description of the issue and then select the Click to edit link to open this knowledge item in the Knowledge Model to resolve the issue.
 |
Once the issues have been resolved, saving the Knowledge Model will update the icons on the Records tab.
Managing existing Knowledge Model objects
You can manage existing Knowledge Model objects by clicking the Options icon:
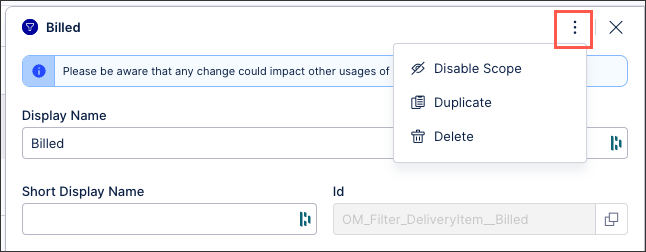 |
You then have the following options per object:
Disable scope: By disabling the scope of an object, the object then can't be used anywhere within the package. This is a good option if you want to disable an object but delete it from your KM.
Duplicate: This opens the create object window with the configuration of the object you are duplicating used as a template. When saving a duplicate object, the object ID must be unique.
Delete: This deletes the object from the KM and any references to that object in existing content. When deleting an object, there is no undo or recovery option.
A record configuration can range from a simple PQL Query to an advanced, customized scheme to retrieve and provide information.
- id: INVOICE
displayName: Invoice
description: ""
pql: BKPF
identifier:
- id: CASE_KEY_ID
displayName: Identifier
description: ""
pql: '"BKPF"."MANDT"'
attributes:
- id: Client_ID
displayName: client_id
description: ""
pql: '"BKPF"."MANDT"'
columnType: INTEGER
unit: ""
format: ""
augmentedAttributes:
- id: STATUS
displayName: Invoice Status
description: ""
columnType: STRING
possibleValues:
- OPEN
- IN_PROGRESS
- CLOSED
defaultValue: OPEN
unit: ""
format: ""
flags:
- id: LOW_INVOICE_VALUE
displayName: Low Invoice Value
description: ""
pql: DAYS_BETWEEN ( ROUND_DAY("BKPF"."BLDAT") ,
PU_LAST(BSEG,ROUND_DAY("_CEL_AP_ACTIVITIES"."EVENTTIME"),
"_CEL_AP_ACTIVITIES"."ACTIVITY_EN"= 'Due Date passed' ))
< 15 AND DAYS_BETWEEN ( ROUND_DAY("BKPF"."BLDAT") ,
PU_LAST(BSEG,ROUND_DAY("_CEL_AP_ACTIVITIES"."EVENTTIME"),
"_CEL_AP_ACTIVITIES"."ACTIVITY_EN"= 'Due Date passed' )) >= 0Let's have a more detailed look at the attributes:
Field name | Description |
|---|---|
id | Defines the id of the record, needs to be unique. |
displayName | Defines the name of the record, should be descriptive. |
description | Possibility to add a short description of the record. |
pql | Here the PQL query gets defined. |
identifier | Defines which element gets used as a unique identifier of the record consists of:
|
attributes | Defines attributes of the record using PQL queries, consists of:
|
unit | Defines the unit of the attribute (e.g. $). |
format | Defines the format of the attribute. |
augmentedAttributes | Defines advanced attributes of a record that go beyond querying information from the data model, consists of:
|
flags | A flag is an attribute of a Record. Record attributes such as the vendor's name can be defined as the root cause feature of a flag. This flag can then be called by an Anomaly. Consists of:
|