Validating KPIs for the object-centric Material Allocation app
In the Material Allocation app’s Knowledge Model, check that all the KPIs (key performance indicators) contain the correct business logic for your organization.
The main Knowledge Model for the Material Allocation app is “Knowledge Model”, which is in the app’s Knowledge Models folder. Work with this Knowledge Model to validate and change KPIs. “Knowledge Model” points to the base Knowledge Model stored in the Celonis Marketplace, which you can’t update directly. Changes that you make to the PQL formulas, KPI names, or formatting in “Knowledge Model” override the base Knowledge Model.
Each KPI in a Knowledge Model contains a PQL (Process Query Language) formula. Some KPIs are reused inside other KPIs as nested formulas. When you adjust the business logic in a single formula, and save it, the change is simultaneously reflected in all the KPIs that reuse the formula.
You work with Knowledge Models in Studio, and any changes you make are applied when you publish a new version of the app. You’ll need Analyst permissions on Studio and the Knowledge Model to modify any of the KPIs and their calculations. If you need training, check out the training track “Build Knowledge Models and Views” on the Celonis Academy.
Here’s how to work with the KPIs in “Knowledge Model”:
In the Celonis navigation menu, select Studio.
Find the Material Allocation app in your Studio space navigation.
Expand the package’s structure using the arrow.
Go to the Knowledge Models folder and select “Knowledge Model”.
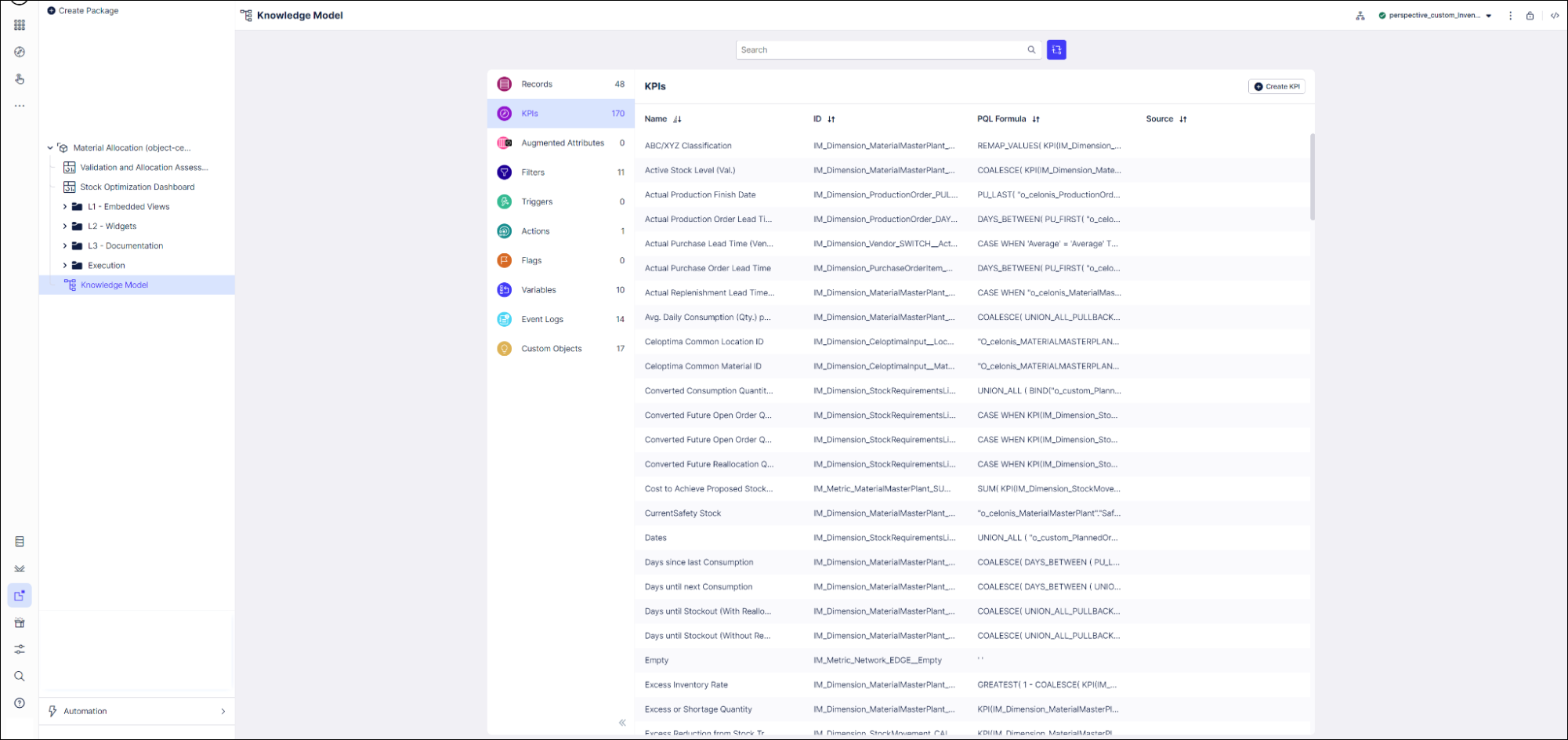
Select the KPIs section of the Knowledge Model.
You can sort and search the KPIs using their name or ID. The prefix to the ID shows what type of component they are. At the end of these instructions, we’ve noted the most important KPIs to check.
To see and edit the full PQL formula and other settings for a KPI, click its row to open an editor. The editor automatically validates any changes that you make in the PQL formula.
If you want a fuller-featured PQL editor that lets you select from the tables and columns in your data, click on the pen icon next to the PQL formula.
If you need to disable a KPI or formula, click the three vertical dots at the top of the editor, and select Disable Scope, then click Disable to confirm. When you do this, the object can't be accessed or used anywhere in the package, including by other apps that depend on it.
When you’ve made changes to the KPIs, use the Publish Package button at the top of the screen in your Studio space to publish a new version of the app.
Here’s a summary for the most important KPIs as they appear in the Knowledge Model:
KPI ID | Formula description |
|---|---|
IM_Dimension_<ObjectName>_INDICATOR__IsOpen | Business logic that indicates if a given order object is considered open. |
IM_Dimension_StockRequirementsListCeloptima _RUNNINGSUM__ProjectedInventoryQuantity | Running sum that computes supply against demand to obtain a projected future inventory based on current confirmed and planned orders in your source system. |
IM_Dimension_MaterialMasterPlant _UNIONALLPULLBACK__DaysUntilStockOutCeloptima | Number of days between the last load date and the first date on which projected inventory will be less than zero. |
IM_Dimension_MaterialMasterPlant_ADD__SupplyFutureValue | Business logic that defines open supply value - by default, this includes valuated inventory, planned orders, purchase requisitions, purchase orders, and production orders. |
IM_Dimension_MaterialMasterPlant_ADD__SupplyFutureQuantity | Business logic that defines open supply quantity - by default, this includes valuated inventory, planned orders, purchase requisitions, purchase orders, and production orders. |
IM_Dimension_MaterialMasterPlant_ADD__ConsumptionFutureValue | Business logic that defines open demand value - by default, this includes reservation orders, sales orders, and independent requirements. |
IM_Dimension_MaterialMasterPlant_ADD__ ConsumptionFutureQuantity | Business logic that defines open demand quantity - by default, this includes reservation orders, sales orders, and independent requirements. |
IM_Dimension_MaterialMasterPlant_CALC__TargetStockQuantity | Sums the initial stock level and the safety stock level to produce the target stock level. Target stock is the threshold above which inventory is considered to be in excess. The initial stock level checks both the minimum lot size and the replenishment lead time multiplied by the consumption, and takes the larger result as the initial stock level. |
IM_Dimension_MaterialMasterPlant_CALC__ExcessSupplyQuantity | Remaining quantity after subtracting Target Stock or Open Demand (whichever is the greater number) from Open Supply. The result is the quantity not needed to satisfy existing demand or inventory targets. If there is Uncovered Demand for the same material plant combination, excess will always be zero. |
IM_Dimension_MaterialMasterPlant_LEAST__UncoveredDemandFutureQuantity | Remaining open demand quantity after all currently open supply has been consumed. If fulfilling open demand requires taking inventory out of Safety Stock, the quantity needed to refill this Safety Stock is considered Uncovered Demand as well. |
IM_Dimension_StockMovement_CALC__WorkingCapitalOptimization | Working capital optimization achieved at the issuing location through acting on a proposed stock transfer. |
IM_Dimension_StockMovement_CALC__SalvagedDemand | Demand value which can be filled at the receiving location through acting on a proposed stock transfer. |