Managing process attributes
Process attributes are descriptive fields and repository objects attached to a process (or sub process) that capture specific information about that process. They help provide context, enable filtering and reporting, and support governance and compliance.
You can edit and assign process attributes by clicking Processes - Architecture and then selecting the main or sub process. This opens up the attribute side panel:
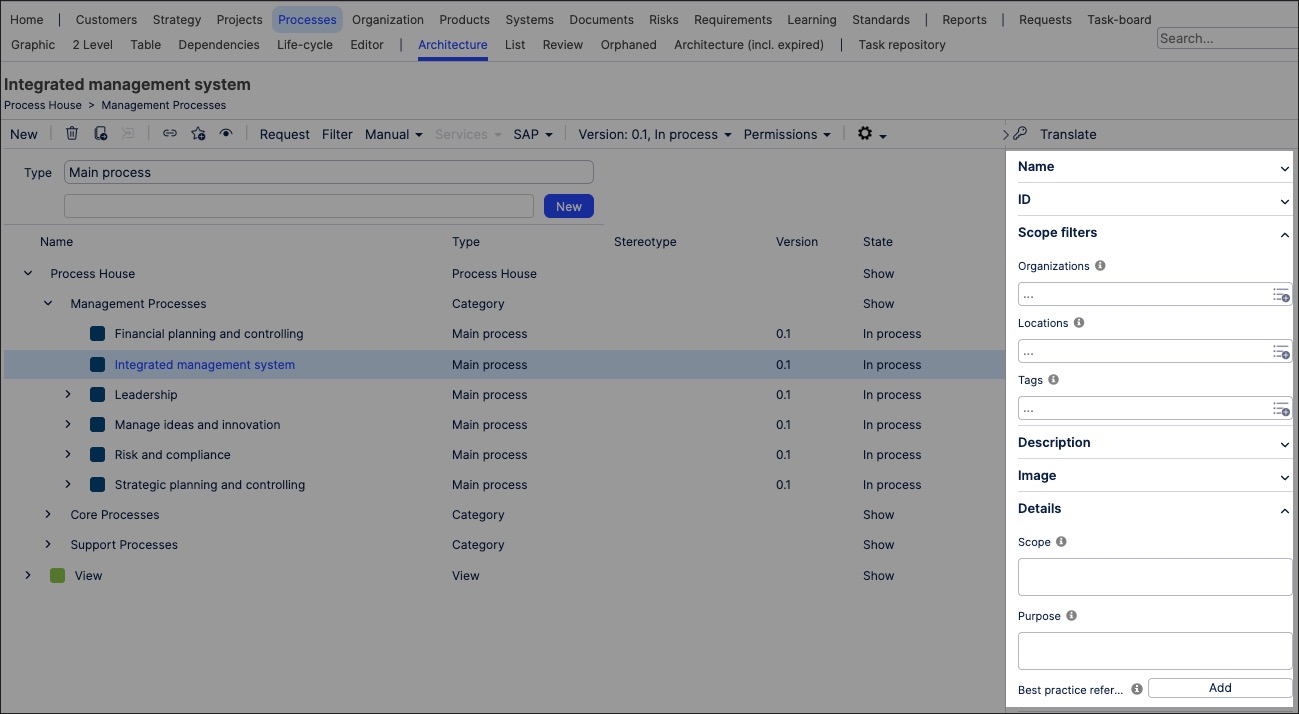
In addition to manually editing process attributes, some attributes will be automatically populated based on your activity within Process Designer. Attributes can also be nested within other attributes, such as related repository objects (for example, locations are nested within organizations).
Available process attributes
Depending on your organization's configuration in Process Designer, your processes can have the following attributes:
Attribute | Description | Link to further content |
|---|---|---|
Accountable Organization | Accountable Organizations represent the organizational units or entities that are responsible for a process, task, or object within your process landscape. You can assign accountable organizations to: Main processes, sub processes, tasks, and other repository objects. | |
Aggregated Maturity | Aggregated Maturity refers to a calculated indicator that reflects the overall maturity level of a process or process landscape, based on the maturity levels of its sub components, such as sub processes or related repository objects (e.g., risks, controls, documentation).
| N/A |
Applications | Applications refer to the IT systems or software tools that support, enable, or automate parts of a business process. Applications are created and managed in the Systems repository object area. | |
Attachments | Add a link,upload a file, or chose to assign existing repository objects to the process. | N/A |
Check Live Data | Checks the configuration of live data within the process. | N/A |
Controls | Controls are formalized governance or compliance mechanisms embedded into processes to mitigate risks, ensure regulatory compliance, and enforce internal policies. Controls are created and managed in the Risks repository object area. | |
Description | Use the rich text editor to add further details about the process. | N/A |
Details | Use the text editor to add scope and purpose information to the process. | N/A |
Documents | Documents are digital or physical artifacts that are linked to business processes, tasks, or objects. They represent information carriers that support, govern, or result from process activities. | |
Glossary | This links to any terms that are defined within the process glossary. | N/A |
Goals | Goals represent the strategic or operational objectives that a process or organization aims to achieve. They help align processes with business strategy and provide purpose and direction for process design and improvement. Goals are created and managed in the KPI repository object area. | |
ID | An ID is a unique identifier assigned to a process or sub process. It helps with version control, traceability, reporting, and integration with external systems like ERP, BPM, or compliance tools. | N/A |
Image | Upload an image file to represent this process. For best quality, upload an image with a ratio of 16:9 and 1300 x 640 pixels resolution. | N/A |
Inputs / outputs | Inputs and outputs represent the information, materials, or triggers that flow into and out of a process or task. They are essential for modeling how processes interact and ensuring clarity, traceability, and efficiency in process execution. Inputs / ouputs are created and managed in the Business Objects repository object area. | |
KPIs | Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are measurable values used to monitor, evaluate, and improve the performance of business processes. They help assess whether a process is meeting its objectives in terms of efficiency, effectiveness, quality, or compliance. | |
Learning units | A Learning Unit is a structured element used to link process knowledge with training content. It helps ensure that employees are trained on the specific processes, procedures, or responsibilities relevant to their roles. Learning units are created and managed in the Learnings repository object area. | |
Locations | Locations refer to organizational or geographical entities where processes, roles, systems, or other elements are situated or carried out. They are used to model and document the physical or logical distribution of process-related resources across different places in your organization. Locations are created and managed in the Organization repository object area. | |
Maturity | Maturity refers to the level of development, completeness, or quality of a process or object (such as a process model, requirement, or documentation). You can manually select the maturity percentage for each process, contributing to the aggregated maturity rating. | N/A |
Measures | Measurements refer to quantifiable indicators used to monitor, evaluate, and improve processes within a business process model. They help assess the efficiency, effectiveness, and compliance of a process. Measures are created and managed in the KPIs repository object area. | |
Milestones | Milestones are key points or significant events within a business process or workflow. They represent important achievements or stages that indicate progress toward completing the process. Milestones help track and monitor the status of a process, ensuring that critical tasks are completed or that certain conditions are met before moving on to the next phase of the workflow. Milestones are created and managed in the KPIs repository object area. | |
Name | A name is a text-based label for the process. | N/A |
Opportunities | Opportunities are essentially the positive or beneficial outcomes that may arise from a situation that is generally viewed as risky. These opportunities are seen as potential ways to turn a risk or uncertainty into a favorable outcome, rather than just focusing on the negative impacts of the risk. Opportunities are created and managed in the Risks repository object area. | |
Participants | Participants are essentially the entities (such as people, roles, or systems) that are involved in the execution of a business process. These participants are responsible for carrying out tasks or interactions within the process flow. Participants are created and managed in the Roles repository object area. | |
Permissions | Permissions control which users and groups of users can view, use, and edit the process. | N/A |
Predecessor / successor process | Predecessor Process - This is a process that occurs before the current process. It either delivers input, sets preconditions, or represents a prior step in a larger end-to-end business process. Successor Process - This is a process that follows the current process. It typically consumes the output or results of the current process and continues the overall flow. | N/A |
Process Cost Analysis | Process Cost Analysis is a feature that helps organizations evaluate and understand the costs associated with their business processes. It allows you to assign, calculate, and analyze costs linked to process steps, roles, resources, or time spent, providing insights into operational efficiency and potential savings. | N/A |
Replace default graphic | This allows you to substitute the standard process visualization (e.g., BPMN diagram or default layout) with a custom image or diagram. This is especially useful for high-level processes like value chains, organizational views, or architecture overviews, where a more tailored graphic can improve clarity or alignment with corporate standards. | N/A |
Requests | Requests typically refer to communication interactions or data exchanges between different processes, roles, or systems. They are used to model and document external triggers or inter-process communications within a business process landscape. Requests are created and managed within the process modeling environment as part of defining interactions between elements. | |
Risk Assessment | Risk Assessment refers to the systematic identification and evaluation of potential risks associated with business processes. It is a key feature used in process modeling and governance to ensure that processes are not only efficient but also compliant and resilient to internal or external threats. | N/A |
Risks | Risks are defined as potential negative events or conditions that could impact a process, project, or organizational goal. They are used to identify, document, and assess uncertainties that might threaten process performance, compliance, quality, or business continuity. | |
Scope filters | Scope filters are used to control the visibility of content within the platform based on defined organizational or contextual boundaries. They help tailor the user experience by showing only the relevant processes, objects, or models to specific users or user groups, depending on their role, department, location, or other defined criteria. | N/A |
Sorting | Enter a numerical value to change the level that the process appears in the process overview. The higher the number, the higher the process appears. | N/A |
Standards | Standards are defined guidelines, rules, or frameworks that processes and activities should comply with to ensure consistency, quality, compliance, and best practices across the organization. | |
Status | A process status indicates the current life cycle stage of a process model within the system. It helps track where a process is in its development, review, and publication cycle, and guides what actions users can take at each stage. While exact statuses can be customized by an organization, the typical default ones include:
| N/A |
Stereotypes | Stereotypes are a way to extend or customize the modeling language used to define processes or workflows. They provide a mechanism to define new types of elements with specialized behavior, properties, or semantics. Essentially, stereotypes enable you to tailor the modeling environment to better reflect the specific requirements or business domain you are working within. | N/A |
Touch Points | Touch points refer to the interactions or connections that a process has with other processes, systems, or stakeholders. They represent critical points of integration, communication, or hand offs where a process interacts with another process or external entity. Touch points help visualize the relationships between different processes, departments, roles, or even external systems, making it easier to understand how a given process fits within the larger business architecture. | N/A |
Trainings | Trainings are typically a set of activities, materials, or resources designed to help users understand and effectively work with the processes and workflows designed within the system. Training is an essential component in ensuring that employees or stakeholders are properly equipped with the knowledge and skills to follow, execute, or manage the business processes. Trainings are created and managed in the Learnings repository object area. |