Task Mining Configuration Editor settings
Note
The Task Mining Client software is versioned and the version number is indicated where relevant. For example, functionality marked as FROM 2.1.3, was introduced in version 2.1.3 of the Task Mining Client software and is not available for versions prior to 2.1.3. For more information about Task Mining software releases, see the Task Mining software installation release notes.
The Configuration Editor settings given here are for the latest version of the Configuration Editor, If you're using an older version, the sections and fields may vary slightly but the possible and default values shoud be the same.
Task Mining Configuration Editor settings
Menu item | Menu option | Description |
|---|---|---|
File | New | Creates a new Task Mining configuration file. |
File | Open | Opens an existing Task Mining configuration file. |
File | Save | Saves the Task Mining configuration file that is currently open. |
File | Save as | Saves the Task Mining configuration file that is currently open under a name and to a location of your choice. |
File | Quit | Exits Configuration Editor. |
Tools | Generate SQL 'CREATE TABLE' query | Generates a SQL query from the Task Mining configuration file. The SQL query is copied to the clipboard. Running this script in a transformation creates the target table in the Celonis Platform. For more information, see Extracting and transforming data. |
Tools | Export JSON (base64 encoded) | Generates a Base64 encoded JSON representation of the Task Mining configuration file and copies it to the clipboard. |
Tools | Import JSON (base64 encoded) | Opens a dialog to import and open a Base64 encoded JSON representation of a Task Mining configuration file. |
About | -- | Contains information about the Task Mining Configuration Editor version and third-party licensing. |
Section | Field | Description | Possible values | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
IBC Upload | Send Data to IBC | Sets whether the captured Task Mining events are:
|
|
Note If IBC Upload is disabled, the other IBC Upload fields are not displayed. |
IBC Upload | Data Pool ID | Identifier of the Celonis Platform Data Pool where captured Task Mining events are stored. | Usually a UUID with this format:
| |
IBC Upload | IBC Team Subdomain | Celonis Platform team subdomain. | Usually the first part of the Celonis Platform URL, for example:
| |
IBC Upload: Send Data to IBC | Server ID | Celonis Platform realm. | Usually the second part of the Celonis Platform URL for example:
| |
IBC Upload: Send Data to IBC | Target Table Name Note The Generate SQL Query button performs the same function as the Generate SQL 'CREATE TABLE' query option in Configuration Editor Application menu > Tools. | Name of the Celonis Platform database table where captured Task Mining events are stored. | -- | |
IBC Upload: Send Data to IBC | Image Service Bucket Name | Name of the bucket where Task Mining screenshots are stored. FROM 1.2.1 | Usually a UUID with this format:
| |
IBC Upload: Send Data to IBC | Update Cloud Period (in Minutes) | Time period (in minutes) during which captured Task Mining events stored in parquet files are sent to the Celonis Platform. | Min value: |
|
Caching | Encrypt Local Data | Sets whether captured Task Mining events temporarily stored on local disk are encrypted. FROM 2.0.4 |
|
|
Caching | Path for Transfer File Cache | Directory where temporary parquet files are stored. If a valid directory isn't specified, the parquet files are stored in the user's temp folder (managed by Windows). Important While UNC paths (e.g. \\server\share) are not supported by default due to security considerations, we can enable them on request if your organization accepts the associated security risk. You can use Windows system variables (like |
| |
Caching | Number of Entries Limit | Maximum number of captured Task Mining events that are cached. If the number of cached events exceeds this value, the cached events are written to a parquet file. | Min value: |
|
Caching | Time Limit in Minutes | Time limit for writing cached events into parquet files (in minutes). If the time limit is exceeded, all cached events are written to parquet. | Min value: |
|
Caching | Timeout in seconds | Time limit for uploading data to the Celonis Platform before terminating the Task Mining Client software. FROM 2.0.4 | Min value: |
|
Caching | Auto Upload Old Cached Files | Sets whether cached files from prevous runs that failed to load are:
FROM 2.4.1 |
|
|
Caching | Maximum Cached File Age (optional) | Number of days cached files are retained before deletion. FROM 2.4.1 | Min value: |
|
Caching | Maximum Cached File Size (optional) | Maximum size of cached image files (in gigabytes). Cached image files are deleted if the maximum size is exceeded. FROM 2.4.1 | Min value: |
|
Compatibility | Use Old Data Push API | Old Data Push API implementation. Important This is included for backwards compatibility only and will be removed in future releases. FROM 1.1.1 DEPRECATED AFTER 1.1.1 |
|
|
Compatibility | Use Old Image Upload API | Old Image Upload API. Important This is included for backwards compatibility only and will be removed in future releases. FROM 1.2.1 DEPRECATED AFTER 1.2.1 |
|
|
Event processing rules define the events, attributes and screenshots that are captured for a Task Mining project. Rules may be based on your use case or legal or privacy requirements so, for example, screenshots might be activated for some applications but not for others where user information may be displayed.
Each event processing rule includes an event, a condition (optional) and an action. If the event and condition meet the criteria specified by the rule, the action is performed.
Where an event and condition match multiple event processing rules, only the action associated with the first event processing rule that matches will be performed. The order you define event processing rules in is therefore important. You should define more specific event processing rules before more general event processing rules.
For example, if you want screenshots to be taken for Microsoft Excel only, the event processing rule specifying this should be ordered before the event processing rule that specifies applications where screenshots will not be taken.A default rule is always included and is applied if none of the actions in the previous event processing rules is performed. The default rule includes an action only.
Important
You must have Chrome browser extensions installed to use event processing rules.
You can create event processing rules in the Configuration Editor using the:
The logic explained in Defining event processing rules, Boolean expressions in event processing rules and Event processing rule examples applies.
Tip
We recommend using the Visual Editor as it’s easier to use and will cover most common use cases. You can, however, switch to the Text Editor at any point although we recommend the Text Editor for more expert users only.
In the Task Mining Configuration Editor, select Event Processing Rules > Visual Editor.
Select New Rule.
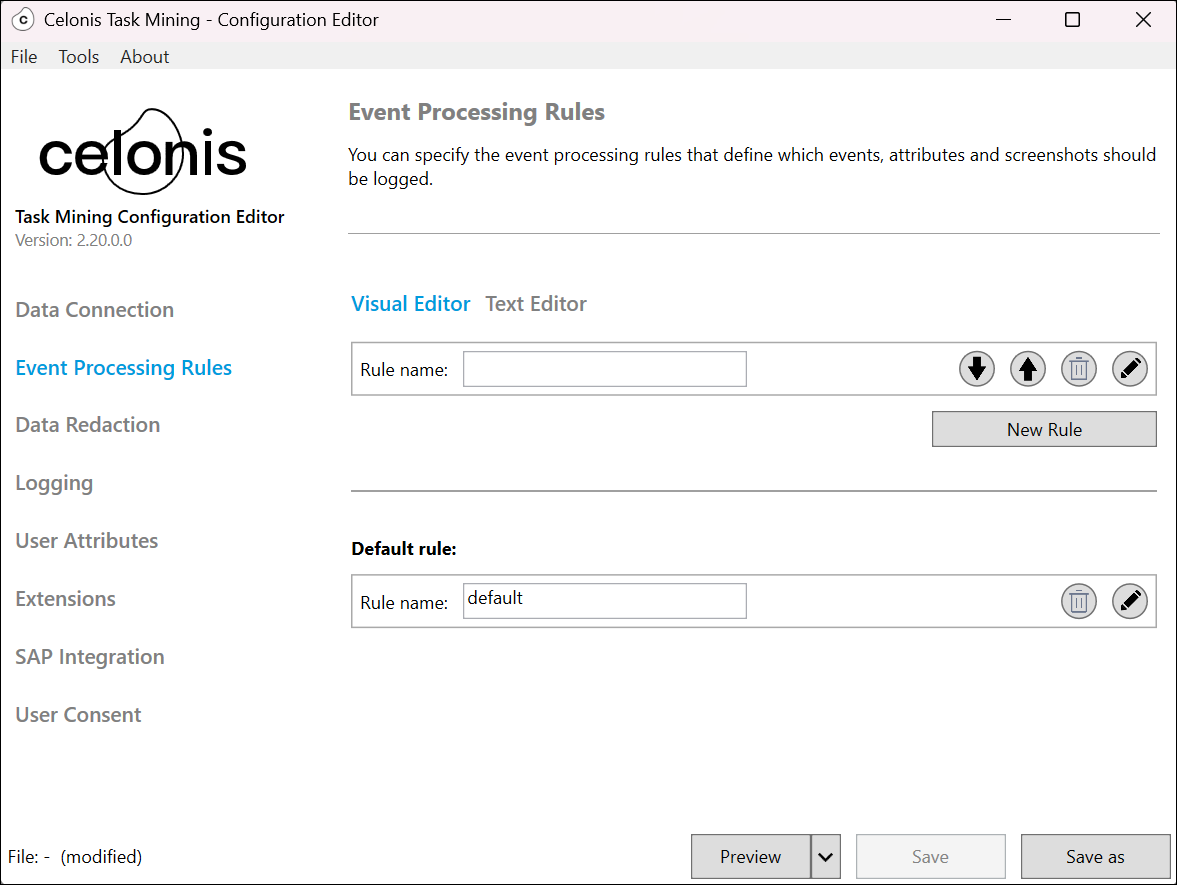
Enter a name for your rule in Rule name.
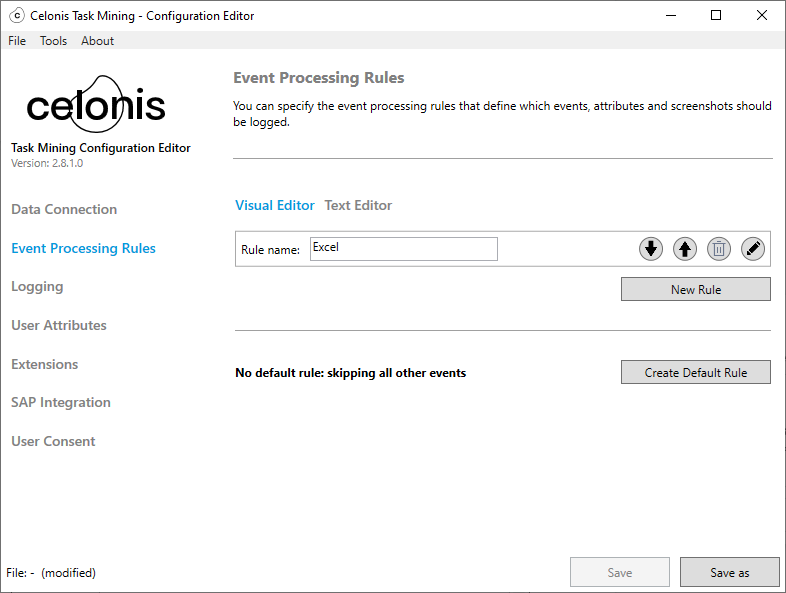
Select the Edit button
 to open the Description screen.
to open the Description screen.Add information about the rule in the Description field.
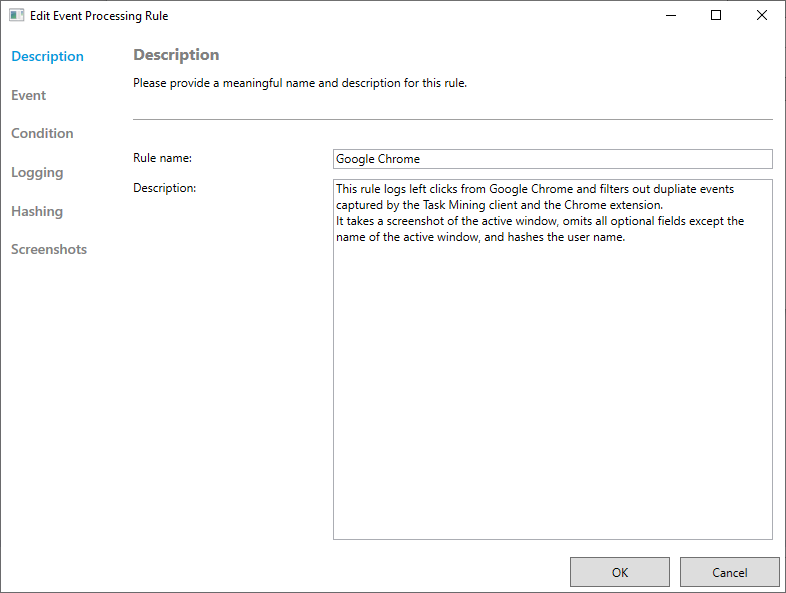
In the sidebar, select Event, Condition, Hashing and Screenshots in turn and specify your rule, using the dropdown menus to help add specific options.
Tip
See Defining event processing rules for more information.
Select OK.
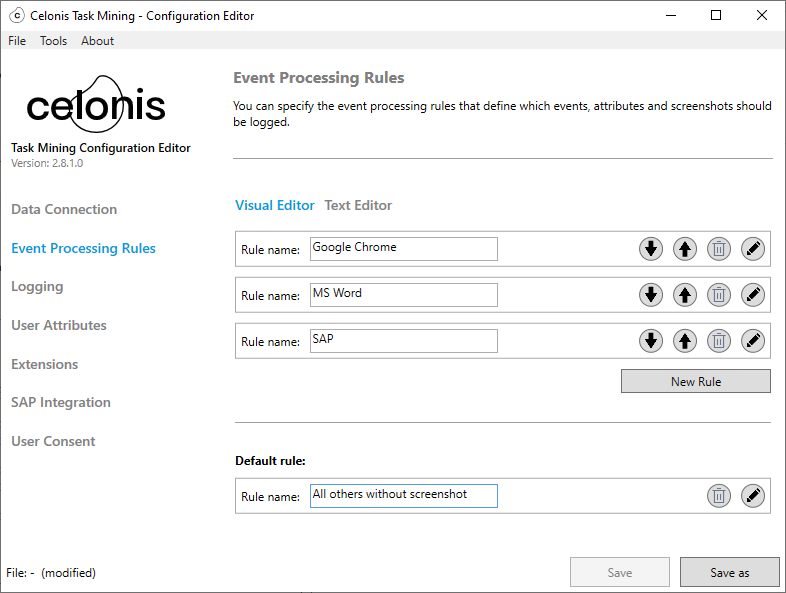
Repeat steps 2 to 7 for each event processing rule you want to add.
Use the Up button
 and Down button
and Down button  to specify the order of your event processing rules.
to specify the order of your event processing rules.Add a default rule.
In the Task Mining Configuration Editor, select Event Processing Rules > Text Editor.
The Text Editor opens.
Add event processing rules in the text field.
See Defining event processing rules for more information.
Important
Event processing rules are case sensitive.
Name | Description | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consists of:
The action is performed when the event and condition meet the criteria defined in the event processing rule. Multiple event processing rules can be specified .If no actions are performed because none of the events and conditions meet the event processing rule criteria, the default rule is applied. A default rule starts with the keyword
If an action is defined in the default rule, it will be performed. If the S |
| The most simple event processing rule consists of the default rule only. This effectively switches off logging for all events:
|
| Consists of:
FROM 1.2.7 |
|
|
| Defines which events will trigger the rule. The rule can be triggered for:
The keyword |
| Trigger the event processing rule for all events:
Trigger the event processing rule for click events only:
Trigger the event processing rule for all events except click events:
|
| Defines a constraint that must be fulfilled for an event to meet the event processing rule criteria. Conditions are defined using Boolean expressions. |
| Trigger the event processing rule only if the event came from the Google Chrome browser:
|
| Defines how an event that matches the rule should be processed. Consists of a definition for:
|
| |
| Defines the event attributes that are logged. All attributes or specific attributes defined in a list of attribute names can be logged. The keyword Note If an attribute isn’t included, the default value (usually null) is used. Mandatory attributes cannot be excluded and will be automatically included even if not specified in the attribute list. For information about mandatory attributes, see the Task Mining attribute reference. |
| Log all attributes:
Log the URL and KeyboardCommand attributes. Mandatory attributes are also logged:
|
| Defines the attributes that are hashed before logging. Can be excluded if hashing of attributes is not required. The hash function used is SHA256. Note Attributes that are excluded from logging are also implicitly excluded from hashing. Adding attributes to the attribute list that are not hashable will cause errors. Mandatory attributes are not hashed. For information about hashable attributes, see the Task Mining attribute reference. |
| Log the
|
| Defines the screenshot capturing mode, with these options:
Can be omitted if screenshots are not required. |
| Take a screenshot of the active window:
Take a screenshot of the active desktop:
Take a screenshot of all desktops:
|
Boolean operator | Description | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compares two expressions and evaluates to a Boolean depending on the comparison operator. Both input expressions must be of the same data type and can be attributes or constant values. Available comparison operators are:
|
| Compare the URL attribute to a string constant for equality:
Check if the
|
| Checks if an expression evaluates to one of the given values. Note All values in the value list must be of the same data type. Supports |
| Check if the
|
| Inverts a Boolean expression. |
| Check whether the URL is not https://www.celonis.com/:
|
| Checks if an expression evaluates to null. The |
| Check if the
Check if the A |
| Computes the logical |
| Check if both comparisons evaluate to true:
|
| Computes the logical |
| Check if at least one of the comparisons evaluates to true:
|
| Allows the logical structuring of Boolean expressions. |
| Logically structure the statement to evaluate the
Evaluate the
|
| Converts the given Supports |
| Convert the value of the
|
| Evaluates if a string expression matches the given pattern. Two different wildcard symbols can be used to define the patterns:
The wildcard symbols can be escaped by a preceding backslash ( \ ), e.g. \% or \_ . The backslash itself is escaped by a double backslash ( \\ ). The comparison is case-insensitive so the patterns |
| Match if the ActiveWindow LIKE '%Unread Messages%' Match if the
Match if the
|
| Maps a URL string to its domain, removing the paths, ports and protocol of the URL. |
| Trims the URL to its domain community.celonis.com:
|
Important
Event processing rules are case sensitive.
Example | Example syntax | Example description |
|---|---|---|
Denylist Slack and do not capture any data. |
| Note The process name for Slack is lower case. If written with a starting capital letter, events from Slack will be captured. |
Collect all events without any restrictions and take a screenshot of the active window. |
or
| -- |
Avoid duplicate events from Google Chrome. |
| Logs all events with all attributes and takes screenshots of the active window, but filters out events from Google Chrome that were not captured by the Chrome browser extension. This avoids duplicate events (like left clicks) that are detected by both the Task Mining Client software and the Chrome browser extension. Tip You can use the same syntax for the Task Mining browser extension for Microsoft Edge by replacing |
Log events from specified applications only. |
| Logs events from Google Chrome, Microsoft Windows Explorer and Slack only. The application name must exactly match the process name displayed in Windows Task Manager without the .exe extension. The application name is case sensitive. |
Don’t log events from specified applications. |
| Events from Google Chrome, Microsoft Windows Explorer and Slack are not logged. The application name must exactly match the process name displayed in Windows Task Manager without the .exe extension. The application name is case sensitive. |
Log events for specified URLs only. |
| Logs events from www.celonis.com and related subdomains (like community.celonis.com) only and takes a screenshot of the active window. |
Collect all events and take screenshots. |
or
| Collects all events without any restrictions and takes a screenshot of the active window. |
Data redaction allows sensitive content, such as personal data, to be removed from captured Task Mining data. You can use basic data redaction or custom data redaction which lets you define regular expressions based on specific use cases.
Data redaction type | Description | Where define |
|---|---|---|
Basic | Predefined data fields are replaced by asterisks. | Enabled by default in the Task Mining Client software basic settings. |
Custom | Define the types of sensitive or personally-identifiable data that are redacted from captured Task Mining using regular expressions (REGEX) and supported variables (optional) provided by the Task Mining Client software. Note Using supported variables simplifies the use and maintenance of regular expressions. | In advanced user settings (Configuration Editor). |
In the Task Mining Configuration Editor, select Data Redaction.
Select New Pattern.
The Data Redaction screen appears.
Enter a:
Name for your data redaction pattern in the Pattern name field.
Description for your data redaction pattern in the Description field.
Regular expression pattern in the Regular expression field.
Tip
For more information, see Regular expressions for data redaction.
Select whether you want to:
Replace data that matches your regular expression with asterisks (default); or
Remove everything except the matched pattern.
Select any attributes you want to redact.
Note
Mandatory attributes cannot be redacted. For more information about which attributes can and can’t be redacted, see the Task Mining attribute reference.
Select OK.
Regular expression | Description | Example: Without data redaction | Example: With data redaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Replaces all Windows usernames with ***.
| Saplogon - TR21 - Profile a.doe | Saplogon - TR21 - Profile *** |
| Replaces all machine names with ***.
| System Settings - LP12392 | System Settings - *** |
| Replaces all email addresses with ***. | Outlook - Draft Mail - t.cookofficial@apple.com | Outlook - Draft Mail - *** |
| Replaces all US social security numbers with‘***. | Adobe Acrobat - Verification 1231-21-2929.pdf | Adobe Acrobat - Verification ***.pdf |
| Replaces the non-domain part of URLs. | https://www.google.com/search?q=testquery | https://www.google.com/*** |
Section | Field | Description | Possible values | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
General | Snippet Split Time | Time period (in seconds) used to split event sequences into snippets. If the elapsed time between two consecutive events exceeds this limit, the later event will be assigned to a new snippet. | Min value: |
|
General | Idle Waiting Time | Time period (in minutes) after which the user is considered absent due to no keyboard or mouse input. FROM 2.4.1 | Min value: |
|
General | Alive Interval | Time between events that are added periodically to the data uploaded to the Celonis Platform to indicate the Task Mining Client is running (in minutes). FROM 2.4.1 | Min value: |
|
General | Use Native URL Retrieval | Sets whether URLs are extracted directly from browsers:
FROM 2.4.1 Note For more information about Chrome and Edge browser extensions, see Task Mining browser extensions overview. |
|
|
General | Show Live Event Monitor in Client | Sets whether the Live Event Monitor menu item in the Task Mining Client software:
Caution When enabled, all users connected to the Task Mining project will have access to the Live Event Monitor. We therefore advise that this is not enabled for productive rollouts but for testing or during the setup phase only. FROM 2.8.1 |
|
|
General | Use UIAA | Sets whether additional information on controls is:
FROM 2.0.4 |
|
|
General | Applications to exclude from UIAA | Applications excluded from additional information extraction by Microsoft UI Automation (UIAA). Tip The application name must exactly match the process name displayed in Windows Task Manager without the .exe extension. The application name is case sensitive. FROM 2.0.4 | -- |
|
Startup Mode | Minimize Task Mining's Window When It Starts | Defines whether the Celonis Task Mining Desktop software starts:
Note The application window can always be restored by clicking the system tray icon. |
|
|
Startup Mode | Startup Mode | Sets whether the Task Mining Desktop software starts the data capture:
Important The Task Mining Desktop software will start to capture data only if the user has already accepted the legal terms. The user can always start or stop Task Mining manually, even if |
|
|
When UIA capture is enabled, the Task Mining Client software acts as a Microsoft UI Automation (UIA) client and captures data from third-party application interfaces. When a user interacts with a UIA-enabled screen element of an application that exposes UIA attributes, data such as field names and values is captured and stored. Applications based on Win32 and .NET programs typically expose UIA attributes.
Note
If you’re using basic client settings, enable the Context of application or webpage in the Captured Details section. This setting is disabled by default.
If you want to use UIA data capture in your Task Mining project, we recommend preliminary testing to determine the quality of data captured. Start with a small representative user sample and validate that the data provided by the third-party application is helpful for your project before rolling it out to more users. This is particularly important if you’re working with in-house custom applications that may not have been previously tested for Task Mining.
Issue | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
The Task Mining Client software cannot reliably capture the UIA data if:
| The closure/ removal of the element means the information on it may already be gone by the time the Task Mining Client software queries it. | User selects:
|
UIA data capture causes a noticeable performance slowdown for some applications in some situations. | According to our testing, applications that must provide UIA data to the Task Mining Client software, as well as performing their standard tasks, may experience performance issues. | Large Microsoft Excel files may cause performance issues so the Task Mining Client software does not send UIA requests to Microsoft Excel by default. |
User attributes are custom attributes that are used to refine Task Mining data. If you define user attributes for team and geographic location, for example, you can analyze your captured Task Mining data at team and geographic location level. A maximum of five user attributes can be defined for each Task Mining project. Once set up, users will be prompted to select user attribute values the next time they start the Task Mining Client software.
User attributes are used in the Team Insights tab of the Workforce Productivity app which is a Studio View. For more information, see the Workforce Productivity app.
Note
When defining user attributes, ensure that individual users cannot be identified by:
Ensuring there are sufficient users per individual attribute value to keep users from being identified.
Assessing whether custom Data Pool permissions should be added to hide users if groups with fewer than five users if required.
Note
You cannot change the name of the custom attribute here.
In the Task Mining Configuration Editor, select User Attributes.
The User Attributes screen appears.
Select the Edit button
 to add a new user attribute or refine an existing user attribute.
to add a new user attribute or refine an existing user attribute.Enter:
A label for your attribute in the Label field.
Values for your attributes in the Values field.
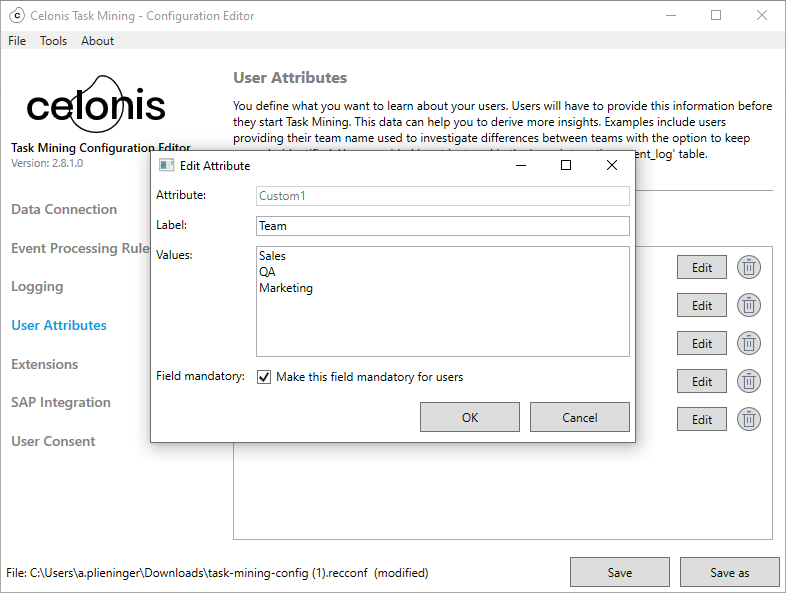
Select the Field mandatory check box to make this a required field.
If selected, users will have to enter this information the next time they start the Task Mining Client software.
Select OK.
In the Task Mining Configuration Editor, select Event Processing Rules.
The Event Processing screen appears.
For each event processing rule:
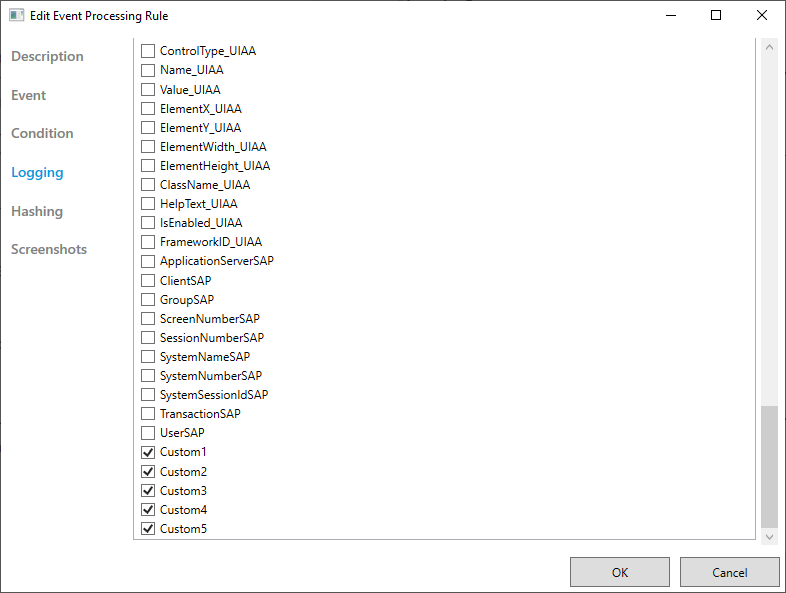
Select the Edit button
 .
.Select Logging.
Ensure any custom attributes you added are selected.
Save and upload your configuration file.
The next time users start the Task Mining Client software, they’ll be prompted to add this information.
Important
To capture event data from Google Chromeand/or Microsoft Edge browsers, you must have Receive Data From All Extensions enabled here and have installed the Task Mining browser extensions.
Extensions are used to extract web page data from websites, even when a user doesn’t interact with the web page data. Custom web page extraction rules define the data that is extracted.
For example, if a user views a Support ticket on a web page, a custom web page extraction rule could extract the Support ticket identifier from the web page. The Support ticket identifier would then be included in the Task Mining data for that user.
Note
Event processing rules capture web page data that a user interacts with. Extension web page extraction rules extract data from web pages that the user doesn’t interact with.
In the Task Mining Configuration Editor, select Extensions.
The Extensions screen appears.
Ensure Receive Data From All Extensions is enabled.
Select Add Rule.
Enter a:
Keyfor your rule in the Key fieldURLfor your rule in the URL field.Pathfor your rule in the Path field.
Note
For more information, see Web page extraction rules.
Select OK.
Visit the URL from step 4 and check your data extractions are working as expected.
Web page extraction rules
Part | Description |
|---|---|
| Identifier for the extracted data item. Must be unique in the Task Mining project configuration file |
| Regular expression that describes the URL of the website the data item should be extracted from. The data item will only be extracted from web pages that match the URL. The regular expression must use JavaScript syntax. |
| Defines which element/value to extract and describes the path of the data item in the document structure of the web page using:
|
Once web page data items have been extracted from web pages using web page extraction rules, they are saved in JSON format in the user interaction event in the WebPageExtractions column. The root element is a list of JSON objects, with each object:
Representing the result of the web page extraction rule.
Consisting of a key attribute that identifies the web page extraction rule and a data attribute that contains the extracted data.
As an XPath expression might return multiple data items, the data attribute is a list of strings, with each string representing a result item from the XPath expression.
Section | Description | Possible values | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
Retrieve SAP Data | Sets the Task Mining Client software to:
Note SAP GUI scripting must be enabled for this to work. For more information, see Configuring SAP for Task Mining integration. FROM 1.2.1 |
|
|
Number of Retry Attempts | Number of times the Task Mining Client software tries to re-establish a lost connection to the SAP GUI. FROM 1.2.1 | Min value: |
|
Waiting Time for Retry | Time the Task Mining Client software waits before trying to re-establish a lost connection to the SAP GUI (in miliseconds). FROM 1.2.1 | Min value: |
|
SAP Process Monitor Interval | Time interval between Task Mining Client software checks for a running SAP GUI instance. FROM 1.2.1 | Min value: |
|
Dynamically Enable Native Windows Dialogs for SAP GUI Scripting | Sets whether native Windows dialogs for SAP GUI scripting is:
Note This setting affects how the SAP GUI works. We recommended enabling it only if users are recording and executing SAP GUI scripts while running Task Mining. |
|
|
Ensure Retrieve SAP Data is enabled in the configuration settings.
Enable GUI scripting on both the client and server sides.
Change the settings using the information in SAP settings for Task Mining integration.
Important
We recommend disabling Notify when a script attaches to SAP GUI and Notify when a script opens a connection in the SAP GUI options. This prevents users being prompted for permission each time the Task Mining Client software starts and tries to connect to the SAP GUI.
SAP settings for Task Mining integration
Location | Setting | Further information |
|---|---|---|
Server side | Set | Applies to all related profiles. |
Server side | Dynamically enable SAP scripting using RZ11 to take effect immediately. | Consult the SAP help for further information. |
Server side | Permanently enable SAP scripting in RZ10 to take effect after a server restart and for future restarts. | Values changed in RZ11 are temporary and lost after a system restart. To make values permanent, you need to change this in RZ10 too.Consult the SAP help for further information. |
Client side | In Accessibility & Scripting >Scripting, enable these options:
| Start the SAP GUI Configuration app to open the settings. |
Note
For information on data privacy and security, see Task Mining data privacy and security.
Section | Possible values | Default value |
|---|---|---|
Consent Text | -- | Placeholder text. |
Link to Additional Information (optional) | -- | -- |
Label of Consent Checkbox |
|